5.14 Normal Model
\[Y \sim N(\mu,\sigma^2)\]
\[f(y)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi \sigma^2}}exp\begin{bmatrix} -\frac{(y-\mu)^2}{2\sigma^2/n}\end{bmatrix}\] for \(y \epsilon (-\infty,\infty)\)
plot_normal(mean,sd)library(bayesrules)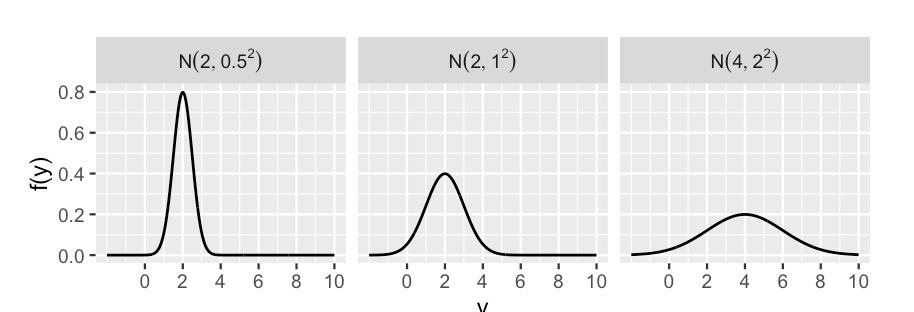
5.14.1 Prior X Likelihood = Posterior
\(f(\vec{y}|\mu)\) x \(L(\mu|\vec{y})\)
Starting from the prior model:
\[\mu \sim N(6.5,0.4^2)\]
We are considering the adults with experience of concussion, in the football dataset.
library(tidyverse)
football%>%head## group years volume
## 1 control 0 6.175
## 2 control 0 6.220
## 3 control 0 6.360
## 4 control 0 6.465
## 5 control 0 6.540
## 6 control 0 6.780football%>%count(group)## group n
## 1 control 25
## 2 fb_concuss 25
## 3 fb_no_concuss 25Let’s see the mean:
football%>%
filter(group == "fb_concuss")%>%
summarise(mean=mean(volume),sd=sd(volume))## mean sd
## 1 5.7346 0.5933976concussion_subjects <- football%>%
filter(group == "fb_concuss")
concussion_subjects%>%
ggplot(aes(x = volume)) +
geom_density()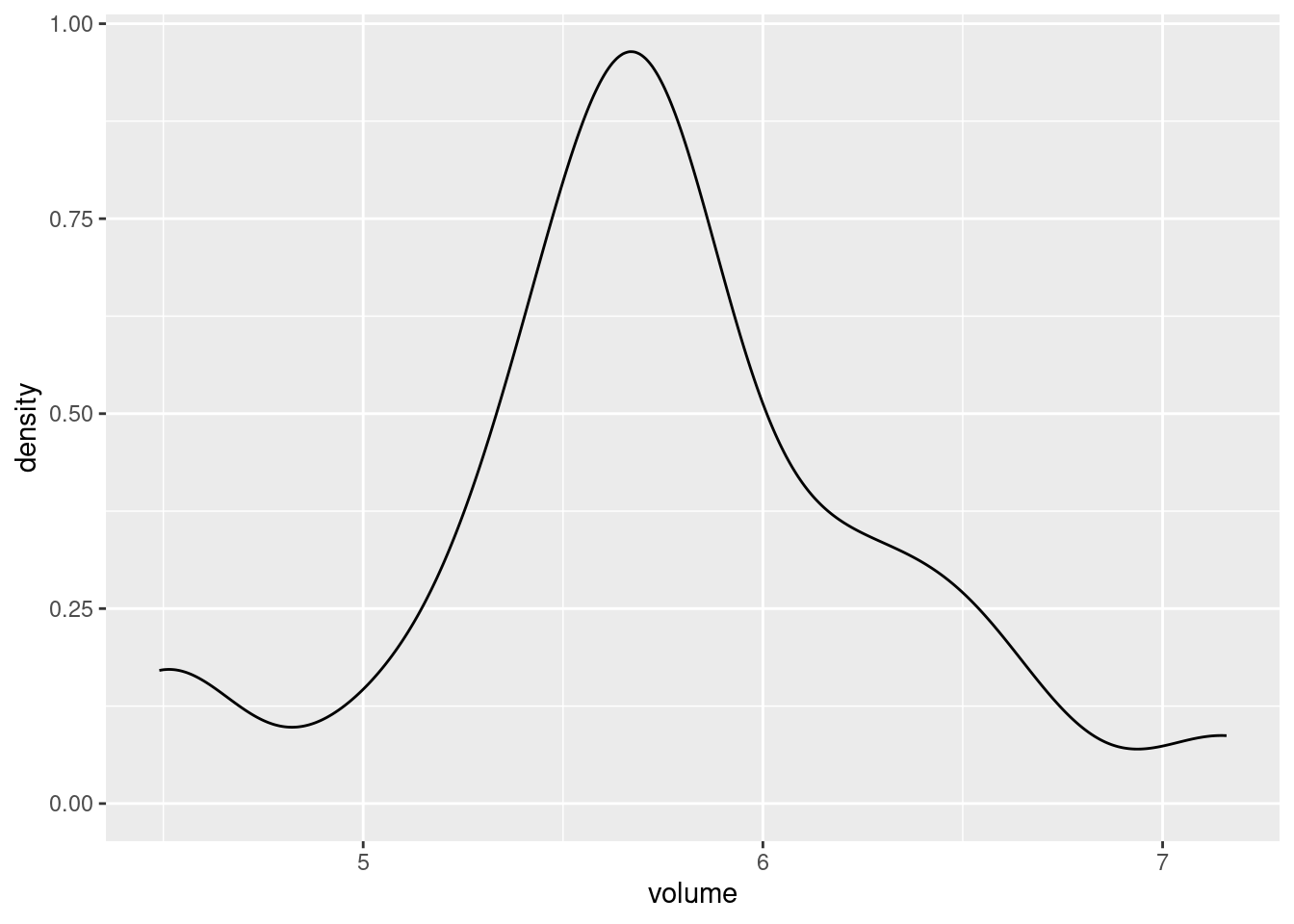
\[L(y|\vec{y}) \propto exp \begin{bmatrix} -\frac{(5.735-\mu)}{2(0.5^2/25)}\end{bmatrix}\]
plot_normal_likelihood(y = concussion_subjects$volume, sigma = 0.5)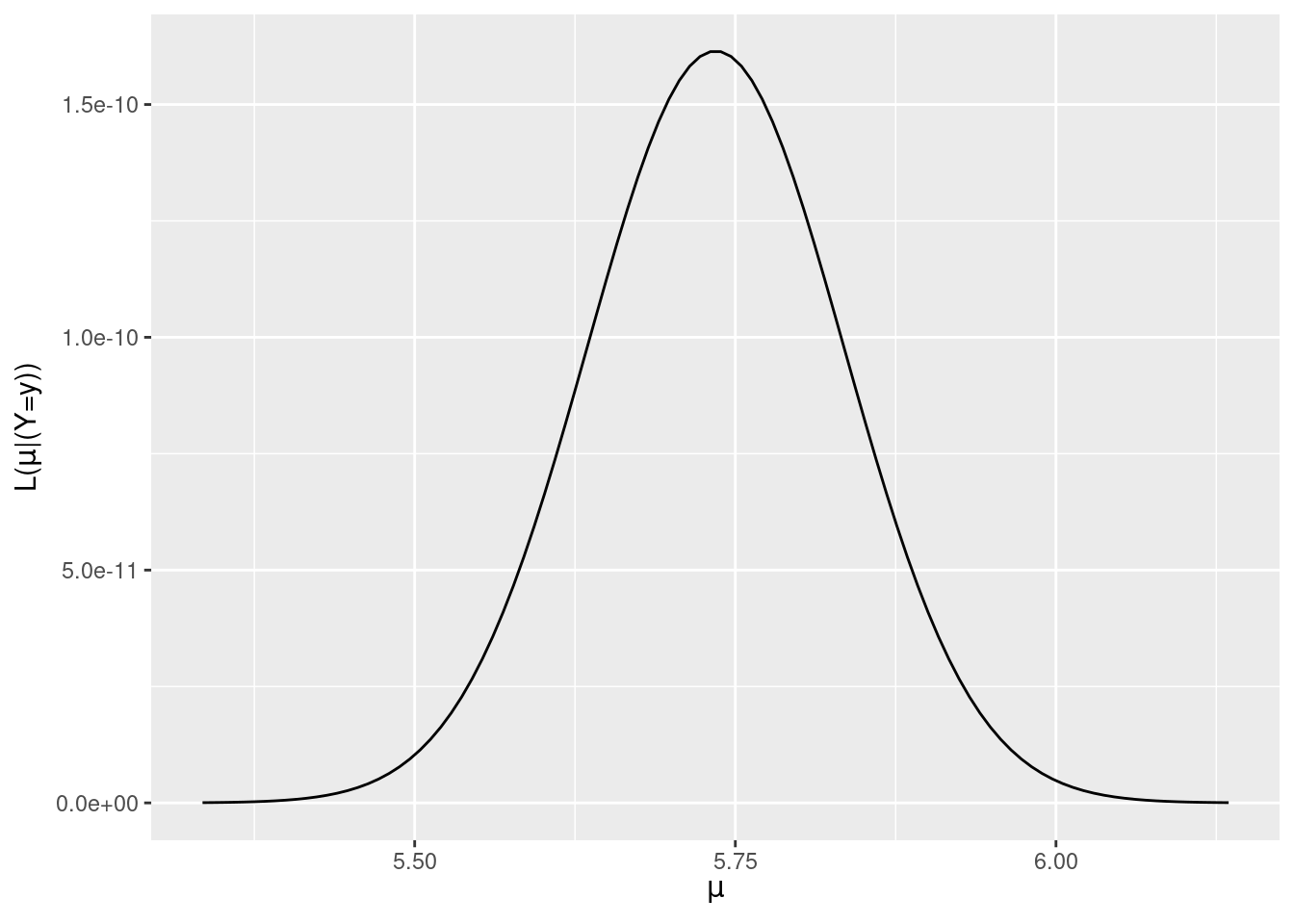
plot_normal_normal(mean = 6.5, sd = 0.4, sigma = 0.5,
y_bar = 5.735, n = 25)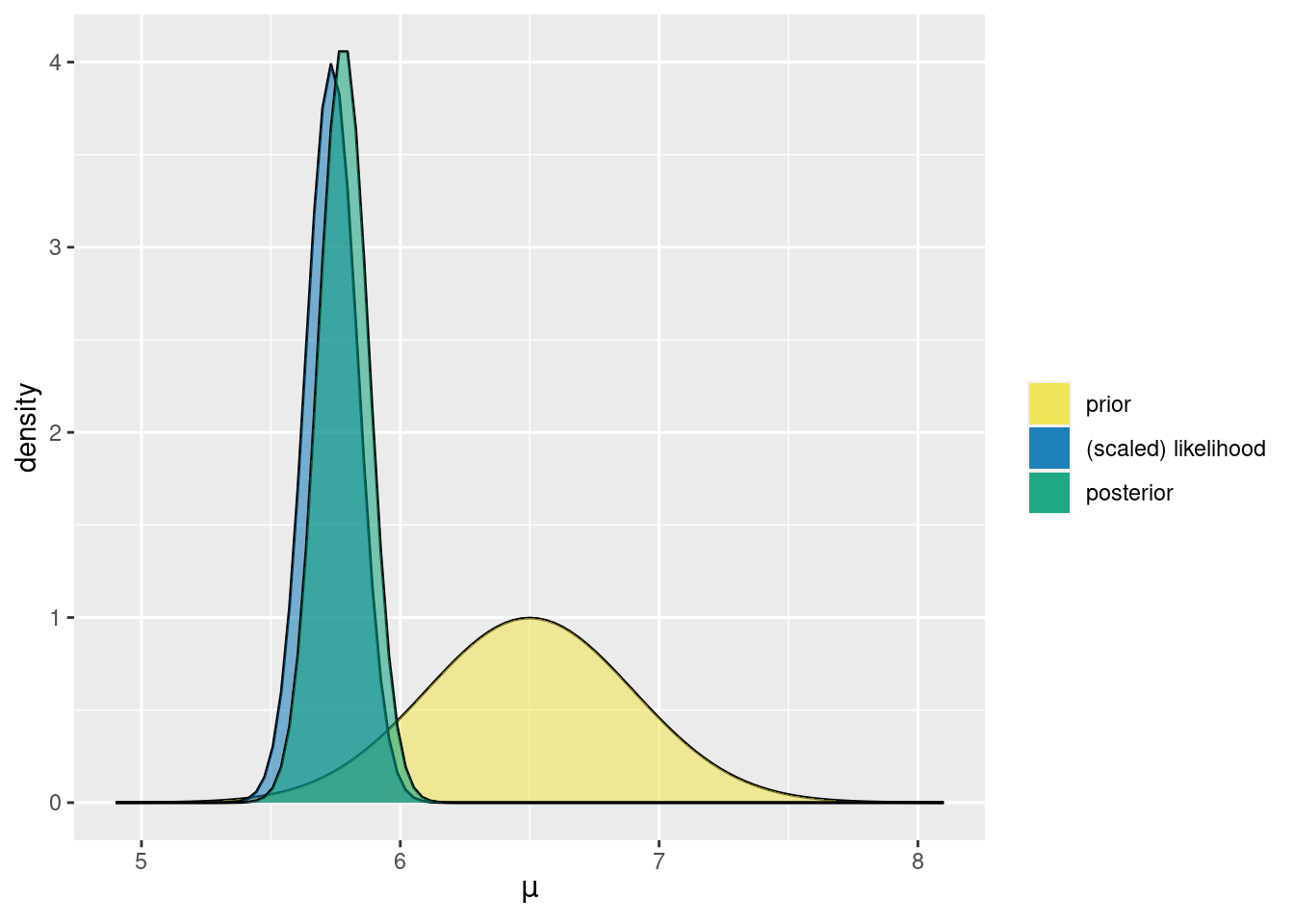
summarize_normal_normal(mean = 6.5, sd = 0.4, sigma = 0.5,
y_bar = 5.735, n = 25)## model mean mode var sd
## 1 prior 6.50 6.50 0.160000000 0.40000000
## 2 posterior 5.78 5.78 0.009411765 0.09701425