11.7 Evaluating predictive accuracy using ELPD
# Calculate ELPD for the 4 models
set.seed(84735)
loo_1 <- loo(weather_model_1)
loo_2 <- loo(weather_model_2)
loo_3 <- loo(weather_model_3)
loo_4 <- loo(weather_model_4)## Warning: Found 1 observation(s) with a pareto_k > 0.7. We recommend calling 'loo' again with argument 'k_threshold = 0.7' in order to calculate the ELPD without the assumption that these observations are negligible. This will refit the model 1 times to compute the ELPDs for the problematic observations directly.# Results
c(loo_1$estimates[1], loo_2$estimates[1],
loo_3$estimates[1], loo_4$estimates[1])## [1] -568.4233 -625.7383 -461.0916 -457.6155# Compare the ELPD for the 4 models
loo_compare(loo_1, loo_2, loo_3, loo_4)## elpd_diff se_diff
## weather_model_4 0.0 0.0
## weather_model_3 -3.5 4.0
## weather_model_1 -110.8 18.1
## weather_model_2 -168.1 21.511.7.1 The bias-variance trade-off
Explore the bias-variance trade-off speaks to the performance of a model across multiple datasets:
- first simulate the posteriors for each model
- calculate raw and cross-validated posterior prediction summaries for each model
# Take 2 separate samples
set.seed(84735)
weather_shuffle <- weather_australia %>%
filter(temp3pm < 30,
location == "Wollongong") %>%
sample_n(nrow(.))
sample_1 <- weather_shuffle %>% head(40)
sample_2 <- weather_shuffle %>% tail(40)g <- ggplot(sample_1, aes(y = temp3pm,
x = day_of_year)) +
geom_point()
g + geom_smooth(method = "lm", se = FALSE)## `geom_smooth()` using formula = 'y ~ x'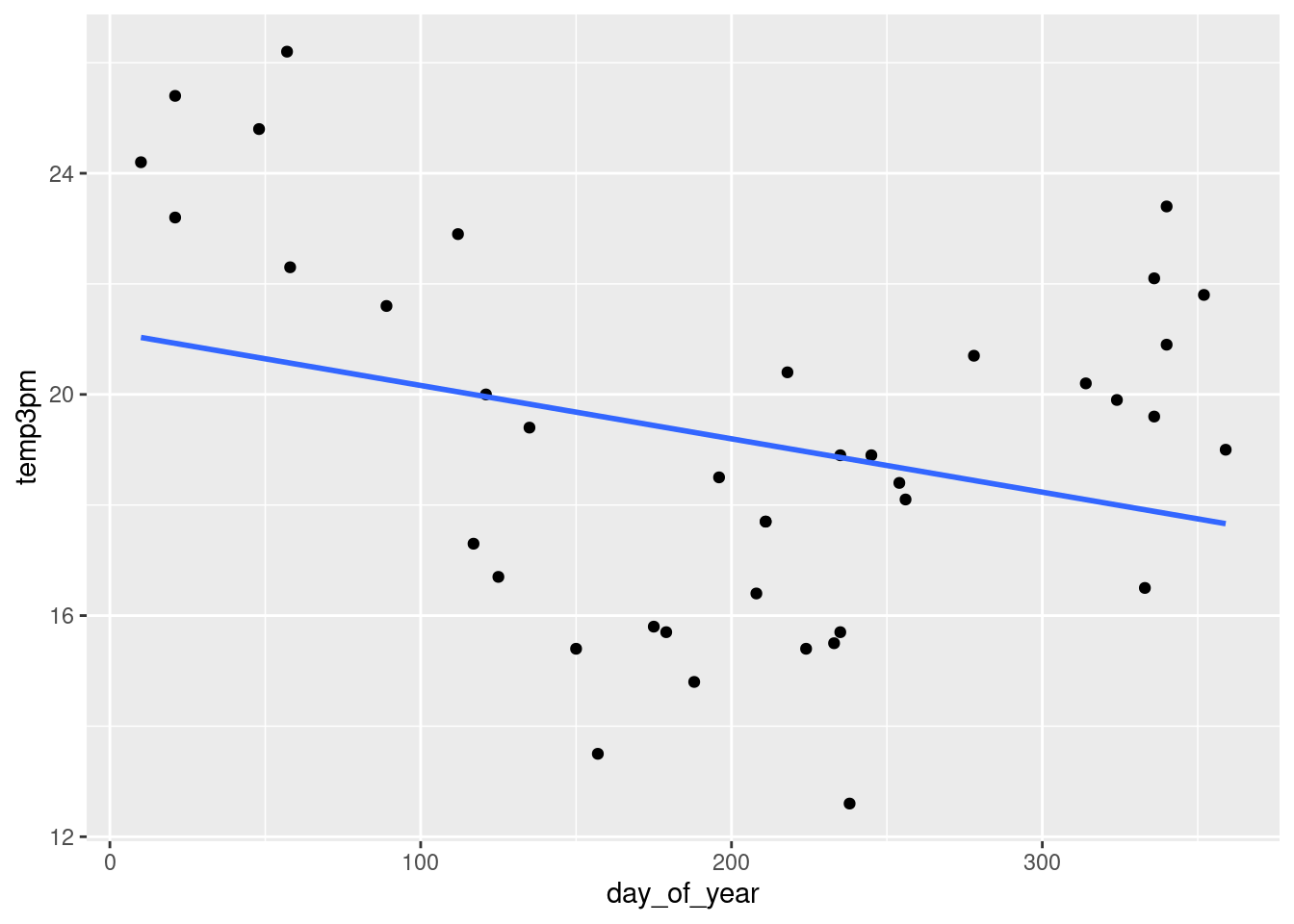
g + stat_smooth(method = "lm",
se = FALSE,
formula = y ~ poly(x, 2))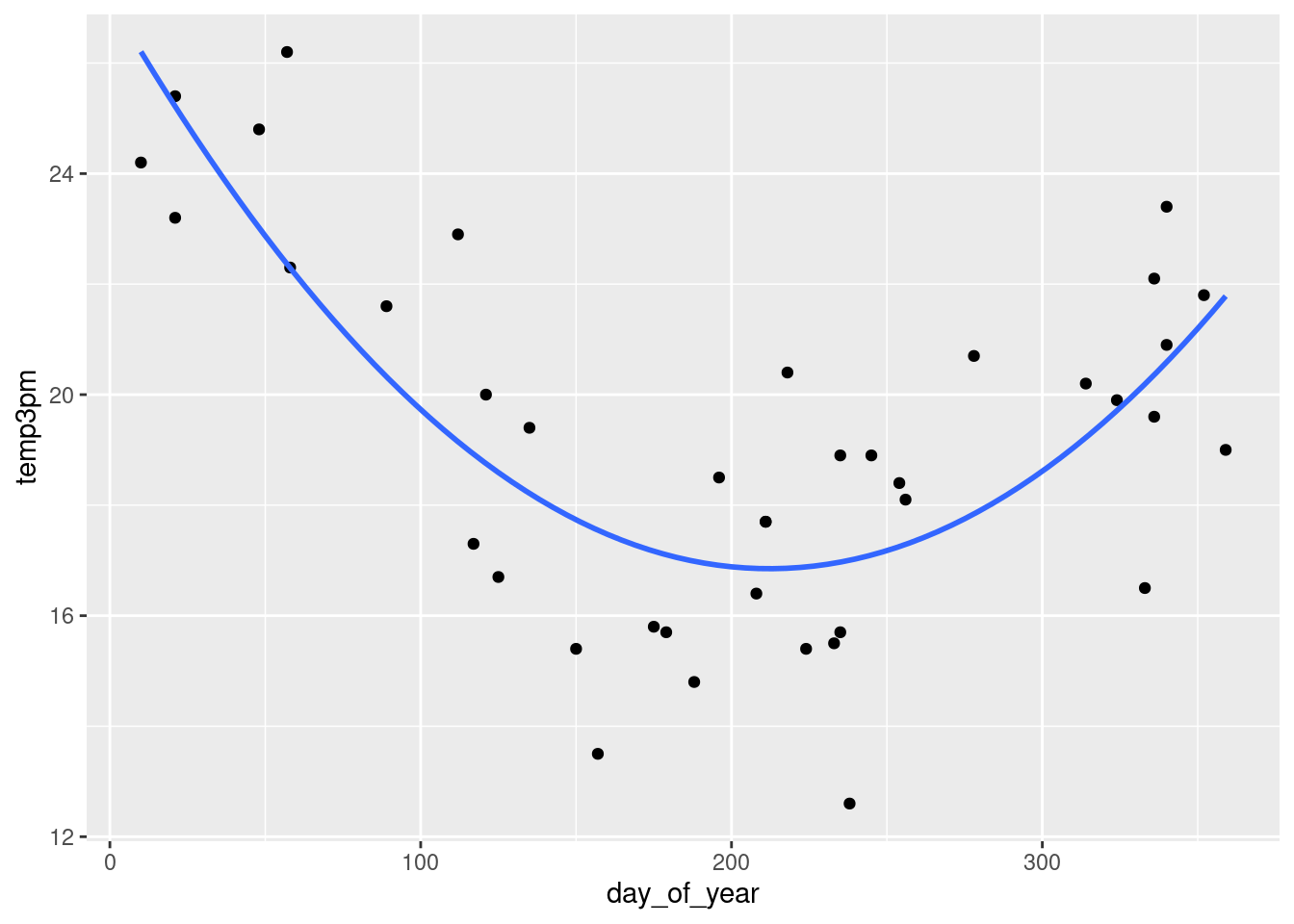
g + stat_smooth(method = "lm",
se = FALSE,
formula = y ~ poly(x, 12))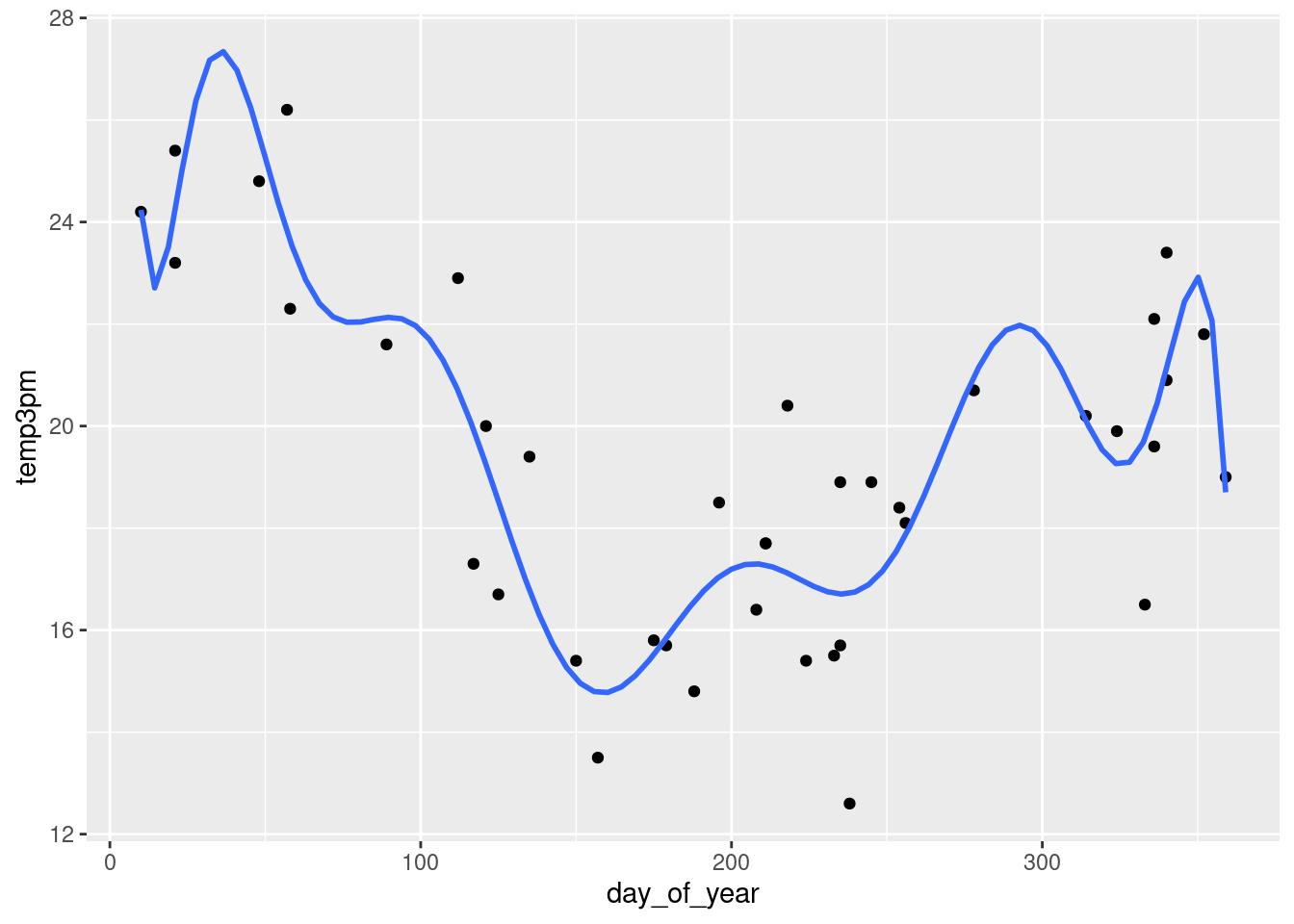
model_1 <- stan_glm(
temp3pm ~ day_of_year,
data = sample_1, family = gaussian,
prior_intercept = normal(25, 5),
prior = normal(0, 2.5, autoscale = TRUE),
prior_aux = exponential(1, autoscale = TRUE),
chains = 4, iter = 5000*2, seed = 84735)
# Ditto the syntax for models 2 and 3
model_2 <- stan_glm(temp3pm ~ poly(day_of_year, 2),
data = sample_1,
family = gaussian,
prior_intercept = normal(25, 5),
prior = normal(0, 2.5,
autoscale = TRUE),
prior_aux = exponential(1, autoscale = TRUE),
chains = 4,
iter = 5000*2,
seed = 84736)
model_3 <- stan_glm(temp3pm ~ poly(day_of_year, 12),
data = sample_1,
family = gaussian,
prior_intercept = normal(25, 5),
prior = normal(0, 2.5,
autoscale = TRUE),
prior_aux = exponential(1, autoscale = TRUE),
chains = 4,
iter = 5000*2,
seed = 84737)set.seed(84735)
prediction_summary(model = model_1, data = sample_1)## mae mae_scaled within_50 within_95
## 1 2.788129 0.819851 0.475 1prediction_summary_cv(model = model_1,
data = sample_1,
k = 10)$cv## mae mae_scaled within_50 within_95
## 1 2.82925 0.8308622 0.475 0.975