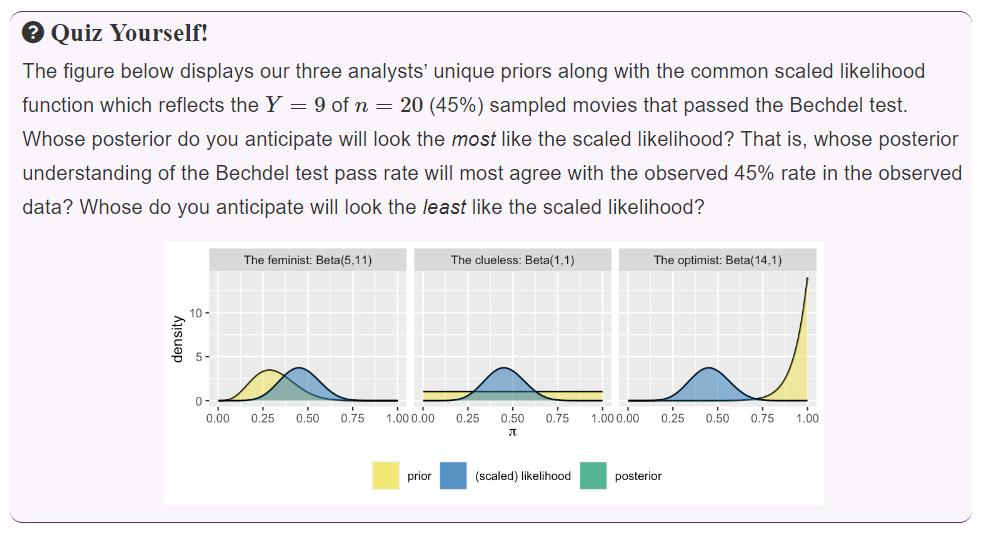
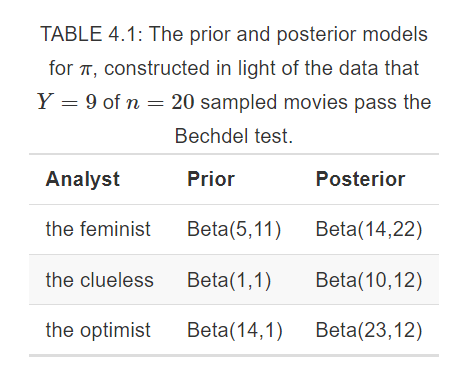
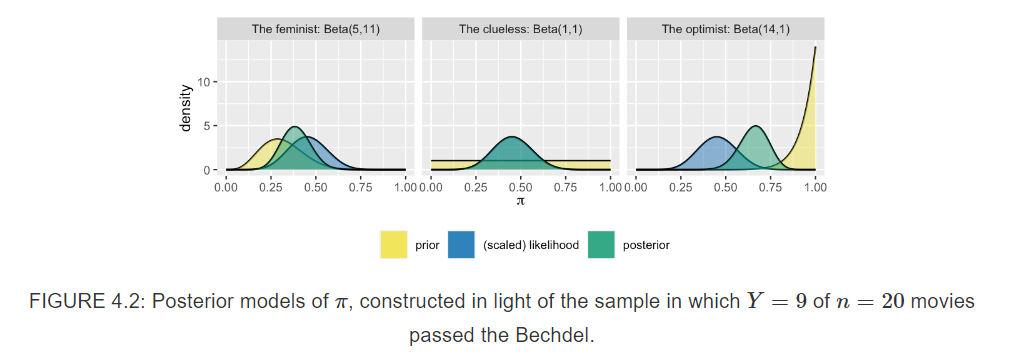
4.2 Different priors, different posteriors
- The more certain the prior information, the smaller the prior variability [Optimist friend].
Informative prior
An informative prior reflects specific information about the unknown variable with high certainty, i.e., low variability.
- The more vague the prior information, the greater the prior variability [Clueless friend].
Vague prior
A vague or diffuse prior reflects little specific information about the unknown variable. A flat prior, which assigns equal prior plausibility to all possible values of the variable, is a special case.
How will their different priors influence the posterior conclusions of the friends? To answer this question, they collected some data!
Review 20 recent movies picked at random.
| year | title | binary |
|---|---|---|
| 2005 | King Kong | FAIL |
| 1983 | Flashdance | PASS |
| 2013 | The Purge | FAIL |
bechdel_20 %>%
tabyl(binary) %>%
adorn_totals("row") %>%
gt() %>%
tab_options(column_labels.font.weight = 'bold')| binary | n | percent |
|---|---|---|
| FAIL | 11 | 0.55 |
| PASS | 9 | 0.45 |
| Total | 20 | 1.00 |