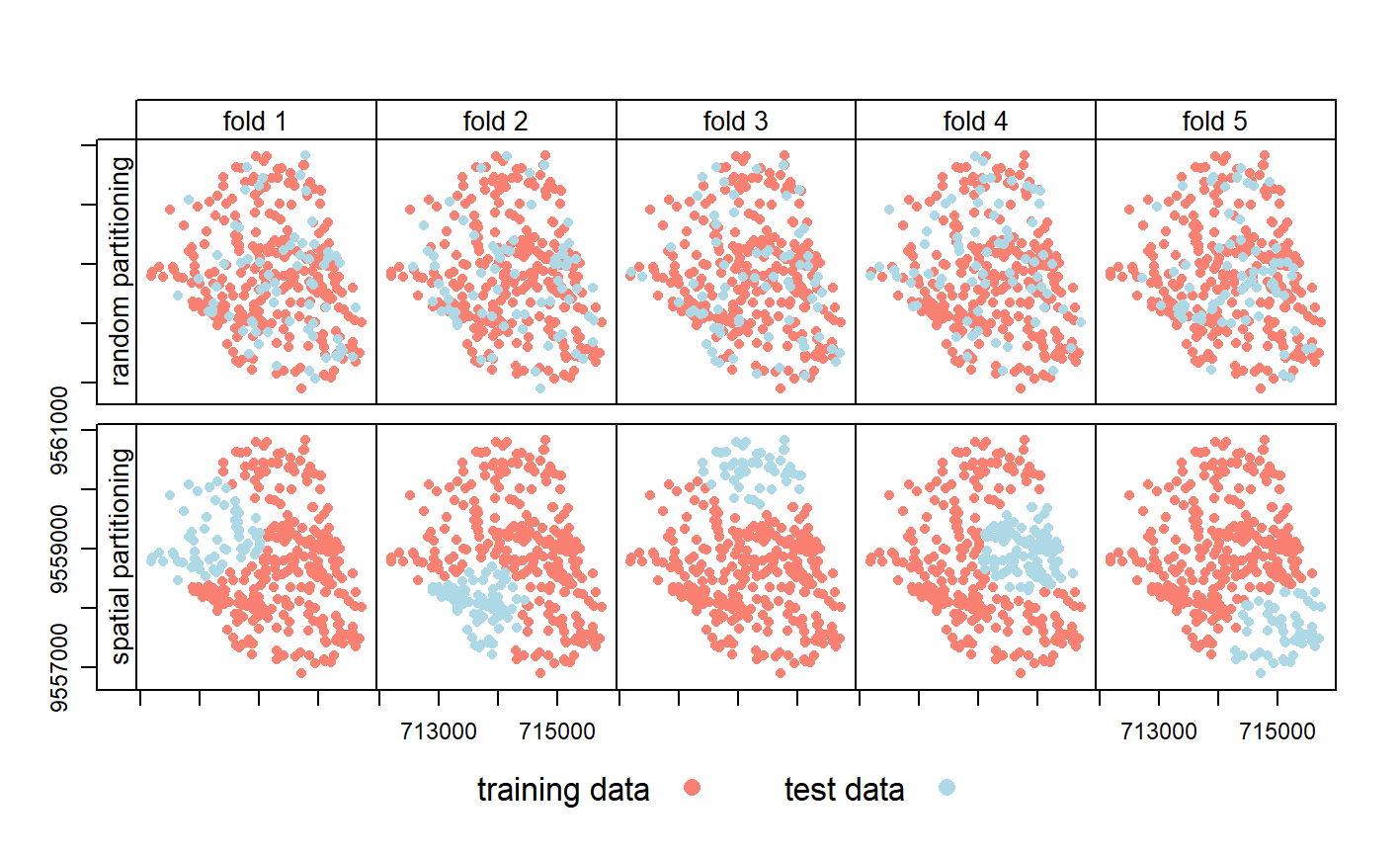
12.4 Spatial Cross-Validation
Cross-validation belongs to the family of resampling methods (James et al. 2013).
- idea is to split (repeatedly) a dataset into training and test sets whereby the training data is used to fit a model which then is applied to the test set.
- Comparing the predicted values with the known response values from the test set (using a performance measure such as the AUROC in the binomial case) gives a bias-reduced assessment of the model’s capability to generalize the learned relationship to independent data.
comparison of CV methods
This means these [geographic data] points are not statistically independent because training and test points in conventional CV are often too close to each other
- To alleviate this problem ‘spatial partitioning’ is used to split the observations into spatially disjointed subsets (using the observations’ coordinates in a k-means clustering; Brenning (2012b)