19.1 Main Concept
- Neural network
- Trained to reproduce the most frequently observed characteristics
- Returns efficient representations of the input data
- Its output layer has the same number neurons as number of inputs it receives.
It can be divided in 2 parts:
- Encoder function \((Z = f(X))\): Converts \(X\) inputs to \(Z\) codings.
- Decoder function \((X' = g(Z))\): Produces a reconstruction of the inputs \((X')\).
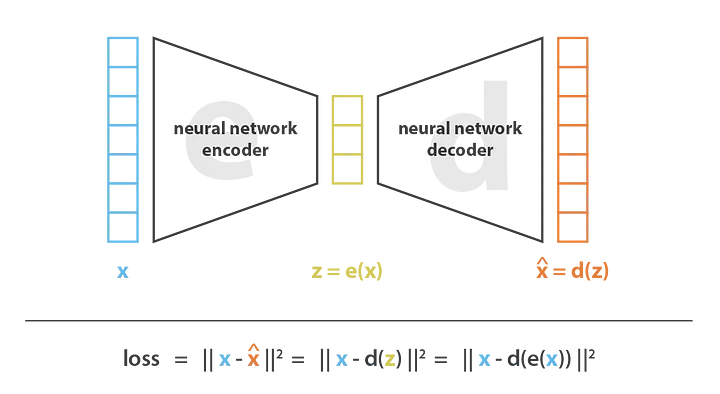
To learn the neuron weights and, thus the codings, the autoencoder seeks to minimize some loss function, such as mean squared error (MSE), that penalizes \(X'\) for being dissimilar from \(X\):
\[ \text{minimize} \; \; L = f(X, X') \]