Explaning the model
MARS is an algorithm that automatically creates a piecewise linear model after grasping the concept of multiple linear regression.
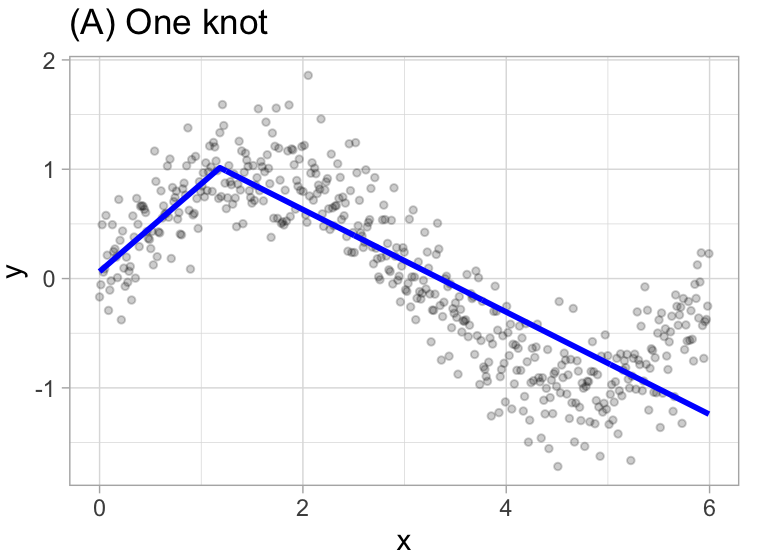
It will first look for the single point across the range of \(X\) values where two different linear relationships between \(Y\) and \(X\) achieve the smallest error (e.g., Sum of Squares Error). What results is known as a hinge function \(h(x-a)\), where \(a\) is the cutpoint value (knot).
For example, let’s use \(1.183606\) the our first knot.
\[ y = \begin{cases} \beta_0 + \beta_1(1.183606 - x) & x < 1.183606, \\ \beta_0 + \beta_1(x - 1.183606) & x < 1.183606 \\ \end{cases} \]
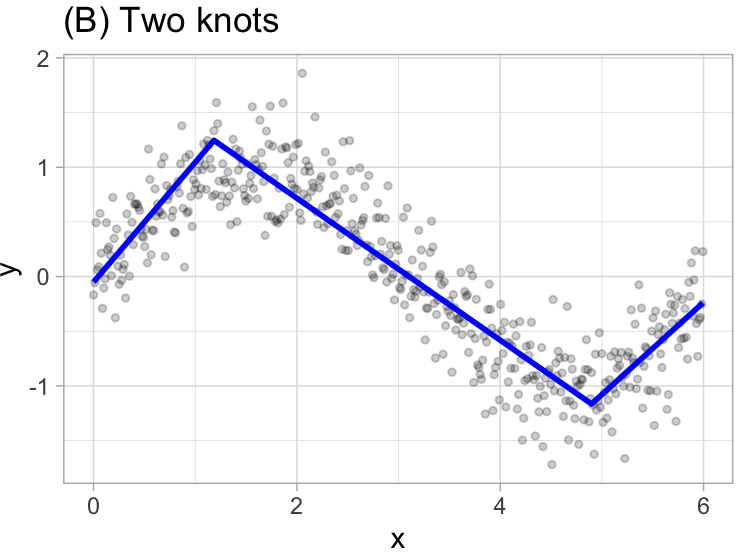
Once the first knot has been found, the search continues for a second knot.
\[ y = \begin{cases} \beta_0 + \beta_1(1.183606 - x) & x < 1.183606, \\ \beta_0 + \beta_1(x - 1.183606) & x < 1.183606 \quad \& \quad x < 4.898114 \\ \beta_0 + \beta_1(4.898114 - x) & x > 4.898114 \end{cases} \]
This procedure continues until \(R^2\) change by less than 0.001.
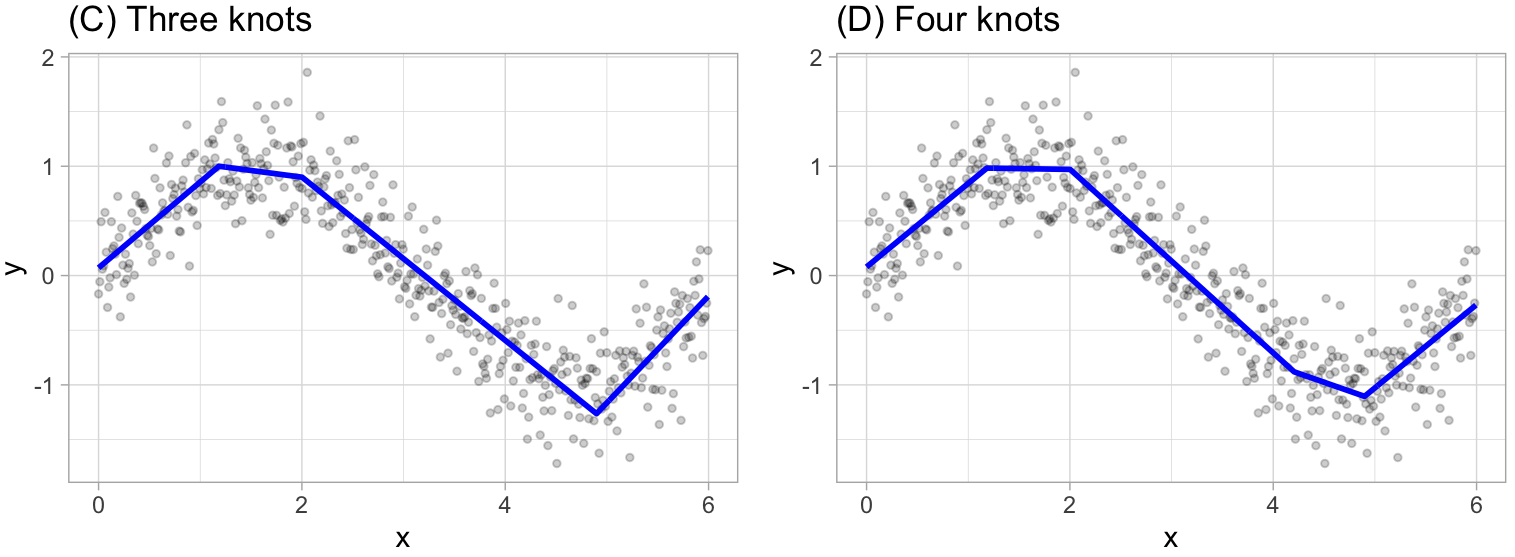
Then the model starts the pruning process, which consist in using cross-validation to remove knots that do not contribute significantly to predictive accuracy. To be more specific the package used in R performs a Generalized cross-validation which is a shortcut for linear models that produces an approximate leave-one-out cross-validation error metric.