12.2 Prophet model
The Prophet model it’s a nonlinear regression model available via the {fable.prophet} package, it works best with time series that have strong seasonality and several seasons of historical data. The model is estimated using a Bayesian approach to allow for automatic selection of the change-points and other model characteristics.
\[y_t=g(t)+s(t)+h(t)+\epsilon_t\]
- \(g(t)\) = piecewise-linear trend (or “growth term”)
- \(s(t)\) = seasonal patterns
- \(h(t)\) = holiday effects
- \(\epsilon_t\) = white noise error term
12.2.1 Case Study 3
Quarterly cement production:
## Loading required package: Rcpp## # A tsibble: 6 x 7 [1Q]
## Quarter Beer Tobacco Bricks Cement Electricity Gas
## <qtr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 1988 Q1 474 6034 428 1418 33142 116
## 2 1988 Q2 440 7389 519 1625 34664 137
## 3 1988 Q3 447 7077 555 1770 37154 157
## 4 1988 Q4 598 6837 538 1791 35303 125
## 5 1989 Q1 467 6051 510 1621 36905 117
## 6 1989 Q2 439 7193 571 1719 37333 149fit3 <- train |>
model(
arima = ARIMA(Cement),
ets = ETS(Cement),
prophet = prophet(Cement ~ season(period = 4,
order = 2,
type = "multiplicative"))
)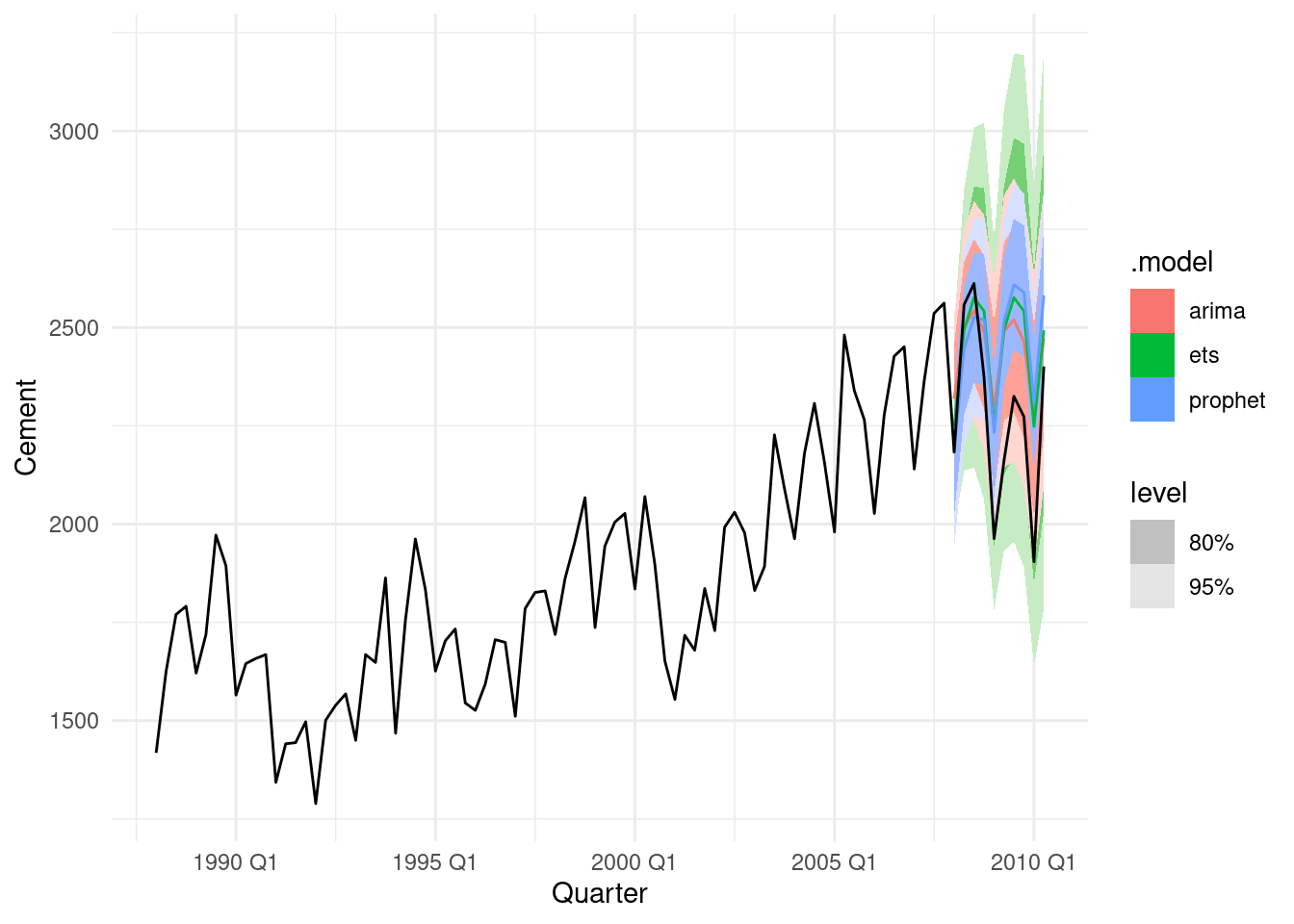
## # A tibble: 3 × 10
## .model .type ME RMSE MAE MPE MAPE MASE RMSSE ACF1
## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 arima Test -161. 216. 186. -7.71 8.68 1.27 1.26 0.387
## 2 ets Test -171. 222. 191. -8.07 8.85 1.30 1.29 0.579
## 3 prophet Test -176. 248. 215. -8.35 9.89 1.47 1.44 0.70212.2.2 Case Study 4
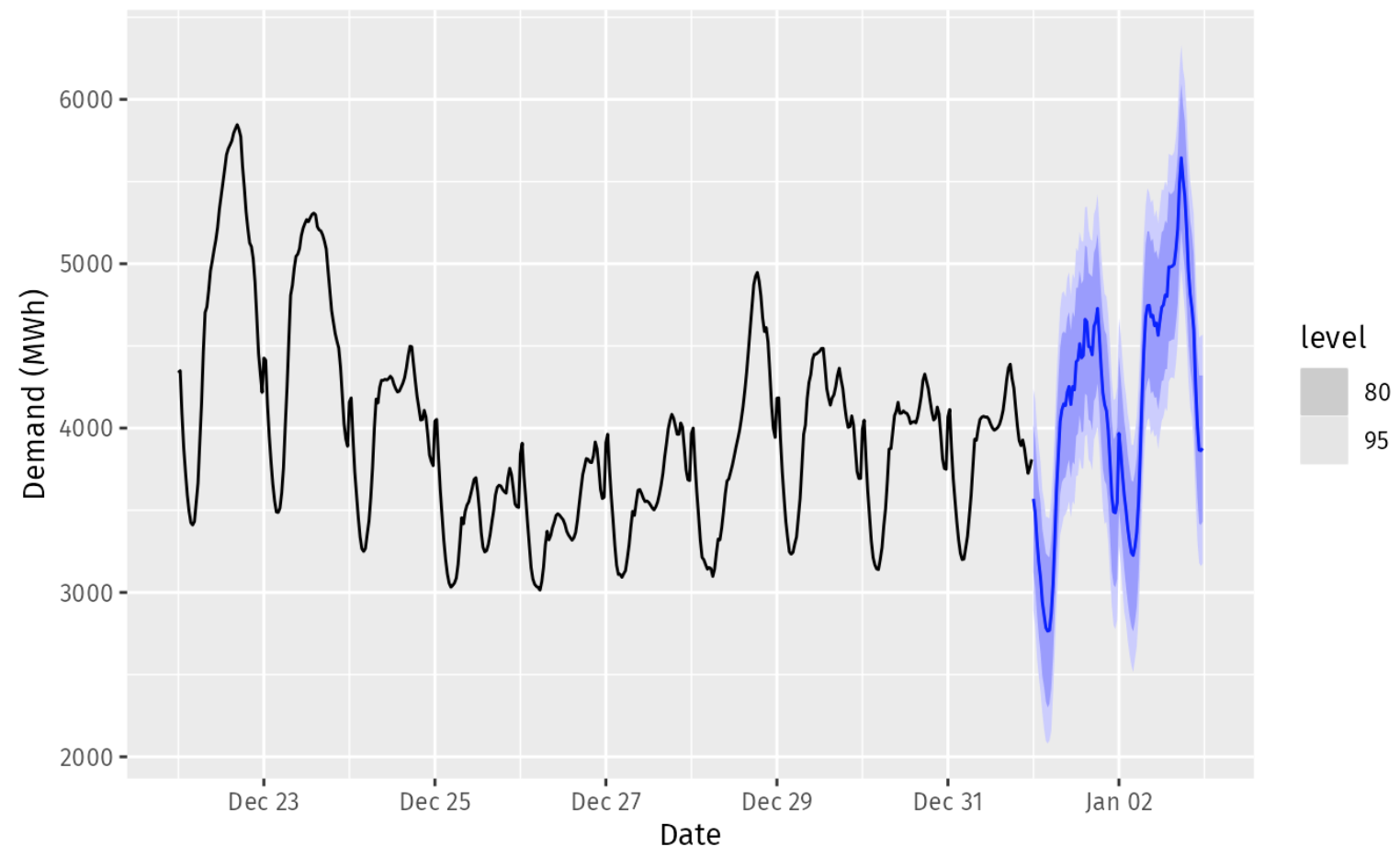
Half-hourly electricity demand:
elec <- vic_elec |>
mutate(
DOW = wday(Date, label = TRUE),
Working_Day = !Holiday & !(DOW %in% c("Sat", "Sun")),
Cooling = pmax(Temperature, 18)
)Faster than Dynamic harmonic regression models (DHR).
The Prophet model adds a piecewise linear time trend which is not really appropriate here as we don’t expect the long term forecasts to continue to follow the downward linear trend at the end of the series.
fit4 <- elec |>
model(
prophet(Demand ~ Temperature + Cooling + Working_Day +
season(period = "day", order = 10) +
season(period = "week", order = 5) +
season(period = "year", order = 3))
)