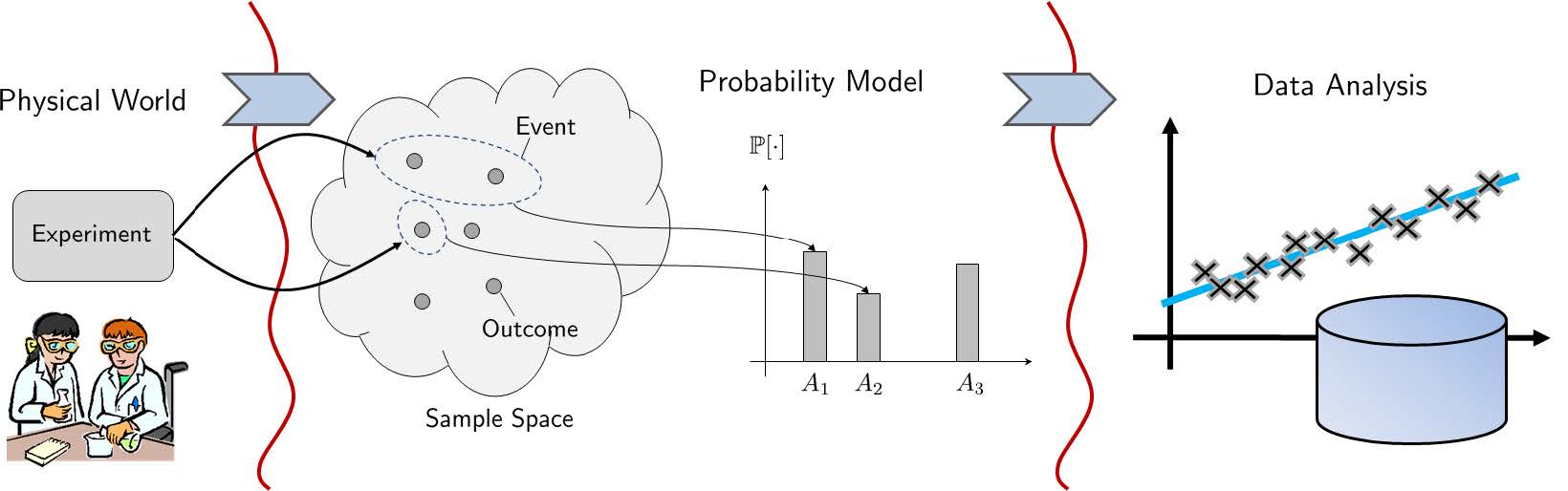
2.2 Probability Space
Three elements constitute a probability space \((\Omega, \mathcal{F}, \mathbb{P})\)
\(\Omega\), the sample space, the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment.
\(\mathcal{F}\), the event space, \(E \subseteq \Omega\)
\(\mathbb{P}\) , the probability law, a measure mapping from an event E to number \(\mathbb{P}[E]\) that satisfies the axioms of probability.