Exponential random variables
- Definition: Let \(X\) be an exponential random variable with parameter \(\lambda > 0\), then:
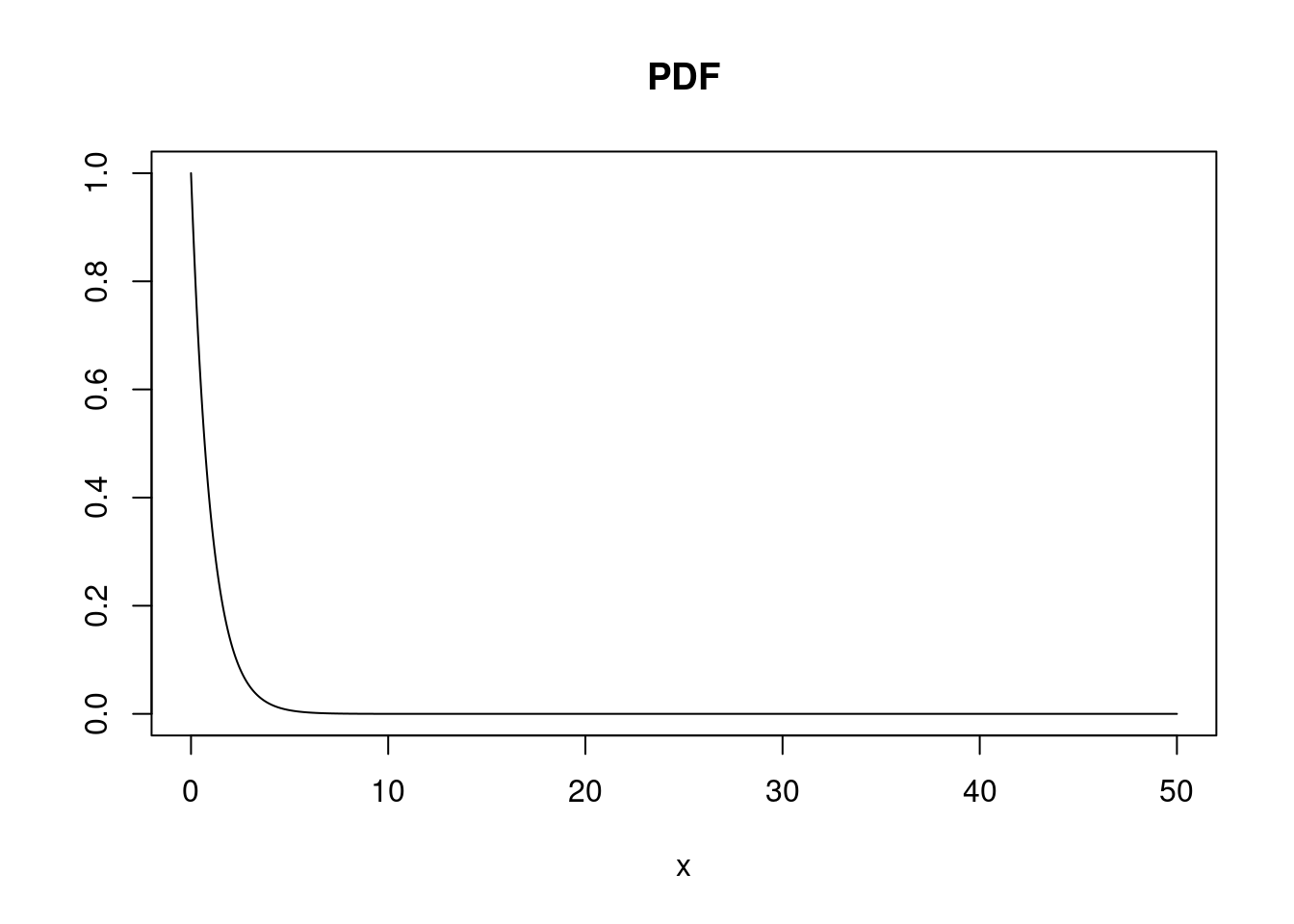
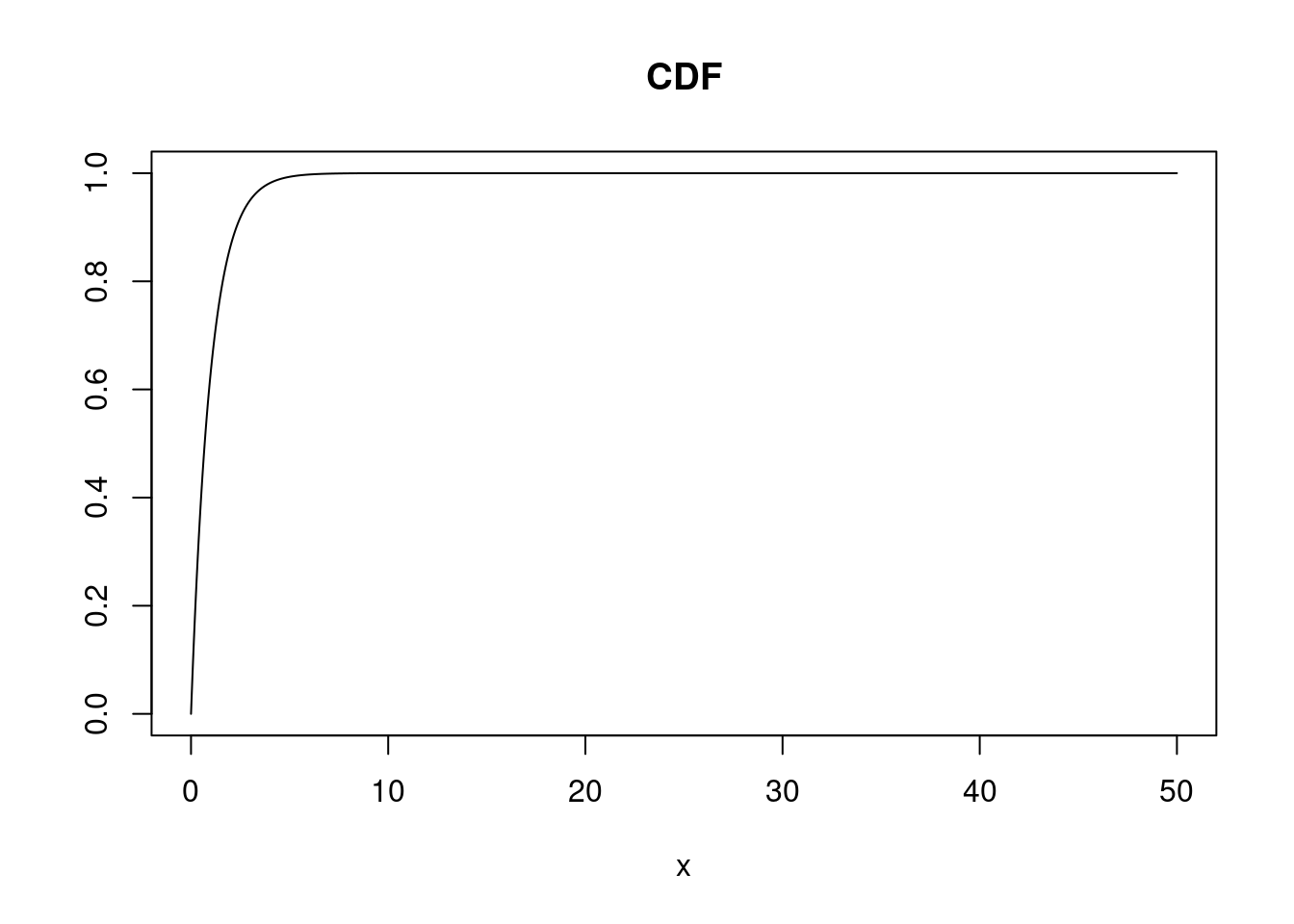
- \(f_X(x) = \lambda e^{-\lambda x}\), if \(x\geq 0\).
- \(f_X(x) = 0\), if \(x<0\).
- \(\lambda\) stands for the rate of decay … larger \(\lambda\), faster decay.
- Notation: \(X \sim Exponential(\lambda)\)
- Theorem: If \(X \sim Exponential(\lambda)\), then:
- \(\mathbb{E}[X] = \dfrac{1}{\lambda}\).
- \(Var[X] = \dfrac{1}{\lambda^2}\).
- Remember that a Poisson random variable describes the number of events that happend in a certain period. Then, an exponential variable is the interarrival time between two consecutive Poisson events; that is, how much time it takes to fo from \(N\) Poisson counts to \(N+1\) Poisson counts.
# Exponential(lambda = 1)
x <- seq(0, 50, 0.01)
lambda <- 1
plot(
x, dexp(x, 1), type = 'l',
main = "PDF", xlab = "x", ylab = ""
)