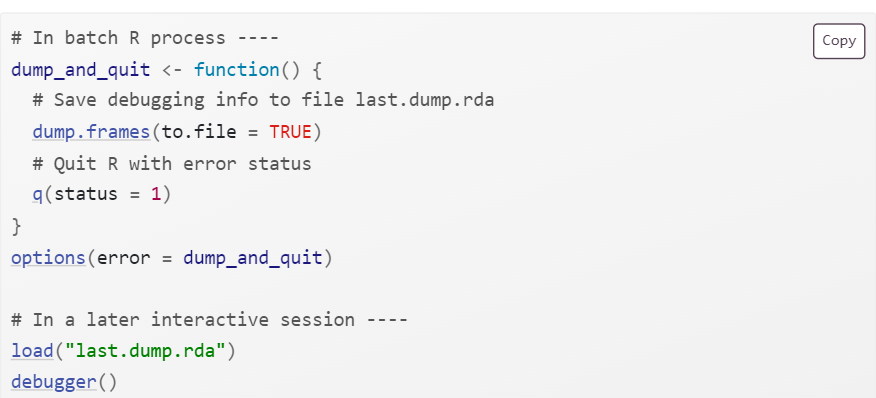
Non-interactive debugging
When you can’t explore interactively…
callr::r()
callr::r(f, list(1, 2)) calls f(1, 2) in a fresh session to help diagnose:
Is the global environment different? Have you loaded different packages? Are objects left from previous sessions causing differences?
Is the working directory different?
Is the
PATHenvironment variable different?Is the
R_LIBSenvironment variable different?
Print debugging
Insert numerous print statements to precisely locate the problem, and see the values of important variables. Print debugging is particularly useful for compiled code.

RMarkdown
If you’re knitting the file using RStudio, switch to calling
rmarkdown::render("path/to/file.Rmd")instead to run the code in the current session.For interactive debugging, you’ll need to call
sink()in the error handler. For example, to userecover()with RMarkdown, you’d put the following code in your setup block: