Locating errors
The most important tool for finding errors is traceback(), which shows you the sequence of calls (also known as the call stack) that lead to the error.
- Here’s a simple example where
f()callsg()callsh()callsi(), which checks if its argument is numeric:
 When we run
When we run f("a") code in RStudio we see:
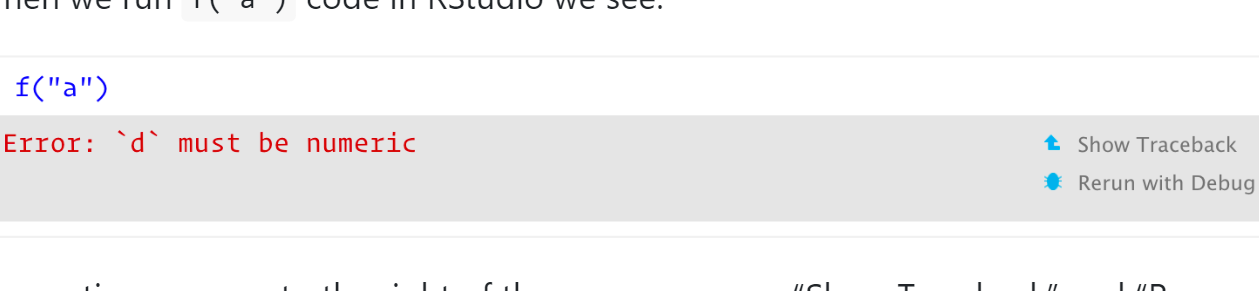
If you click “Show traceback” you see:

You read the traceback() output from bottom to top: the initial call is f(), which calls g(), then h(), then i(), which triggers the error.