6.3.2.3 Optimization with Tidymodels
- Hyperparameters can be tuned to improve model performance.
For a random forest model, these can be:
Number of trees.
Number of variables to consider at each split.
Minimum number of data points required to split a node.
The {tidymodels} package makes this process easier.
# Spending data
set.seed(1231) # Set seed for reproducibility
# Split the data into training and testing sets
split <- initial_split(simulated_data, prop = 0.8)
train_data <- training(split)
test_data <- testing(split)
# Create a resampling scheme: 5-fold cross-validation
#
cv_folds <- vfold_cv(train_data, v = 5)
# Create a recipe for data preprocessing
data_recipe <- recipe(I ~ ., data = train_data) %>%
step_nzv(all_predictors()) %>%
step_normalize(all_numeric())
# Define the Random Forest model
rf_ranger_model <-
# tuning parameters - Machine Learning Application
rand_forest(trees = tune(),
min_n = tune()) %>%
set_engine("ranger") %>%
set_mode("regression")Bayesian Optimisation
Bayes Theorem
\[Pr(B|A) = \frac{Pr(A|B)*Pr(B)}{Pr(A)}\] \(A\) and \(B\) are events and \(B\) \(\neq\) \(0\)
# Bayesian optimization
set.seed(123)
bayes_results <- tune_bayes(rf_ranger_model,
data_recipe,
resamples = cv_folds,
metrics = metric_set(yardstick::rmse, yardstick::rsq),
# Number of initial random points
initial = 5,
# Total iterations including initial points
iter = 20,
param_info = parameters(rf_ranger_model))The show_best() function displays the best hyperparameters based on the optimization results.
## # A tibble: 5 × 9
## trees min_n .metric .estimator mean n std_err .config .iter
## <int> <int> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr> <int>
## 1 1993 2 rmse standard 0.0325 5 0.00697 Iter9 9
## 2 1574 2 rmse standard 0.0326 5 0.00665 Iter15 15
## 3 1387 2 rmse standard 0.0326 5 0.00688 Iter14 14
## 4 1932 2 rmse standard 0.0329 5 0.00683 Iter8 8
## 5 1257 2 rmse standard 0.0333 5 0.00655 Iter19 19Extract the best parameters:
## # A tibble: 1 × 3
## trees min_n .config
## <int> <int> <chr>
## 1 1993 2 Iter9The
fit()function fits the model using the best hyperparameters.The
predict()function makes predictions on the test data.
# Final model with best parameters
final_bayes_model <- finalize_model(rf_ranger_model,
best_bayes)
final_fit <- fit(final_bayes_model,
formula = I ~ .,
data = train_data)
# Predict and evaluate on test data
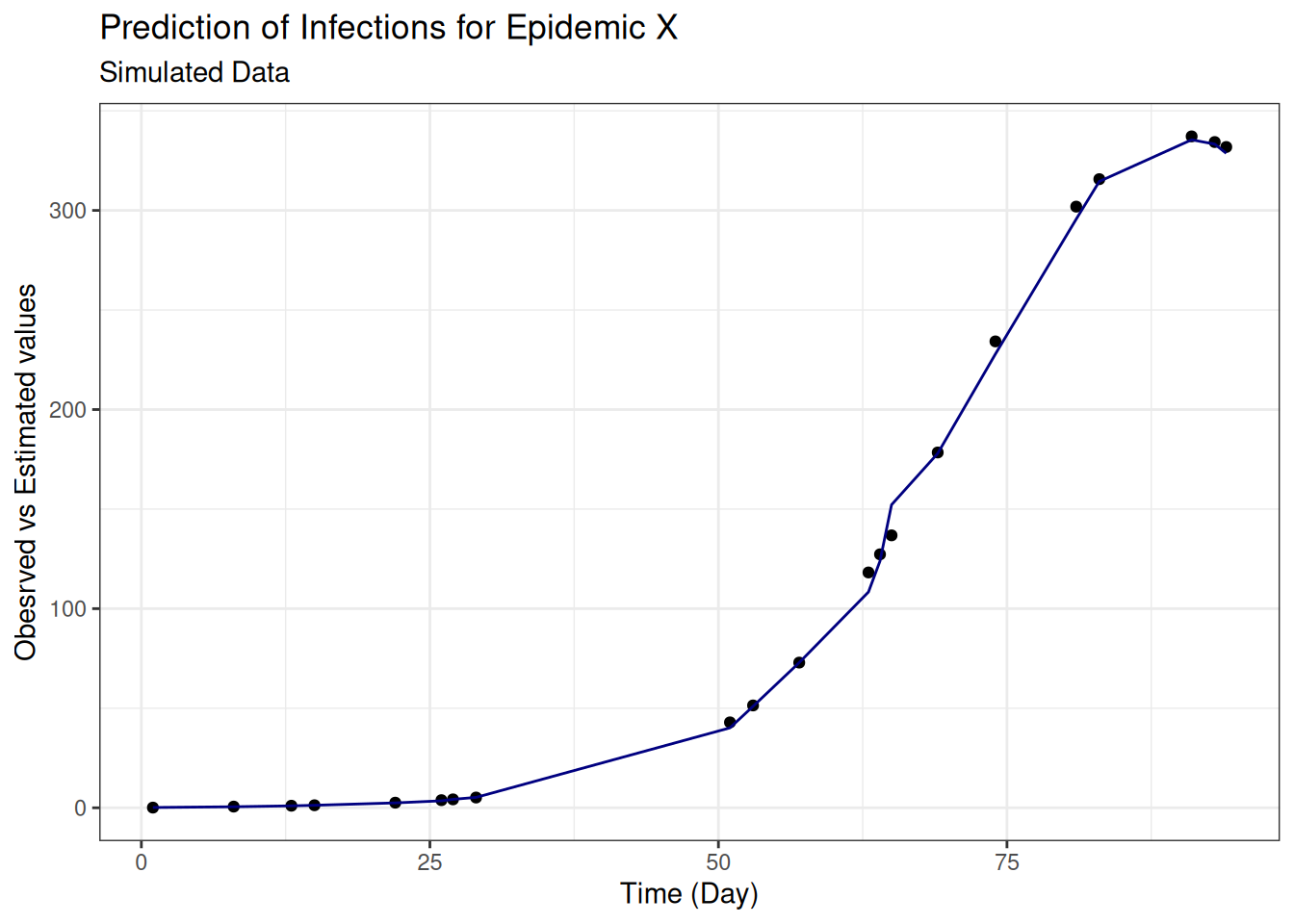
predictions <- predict(final_fit, new_data = test_data)
augumented <- augment(final_fit, new_data = test_data)
eval_metrics <- metrics(estimate = .pred,
truth = I,
data = augumented)
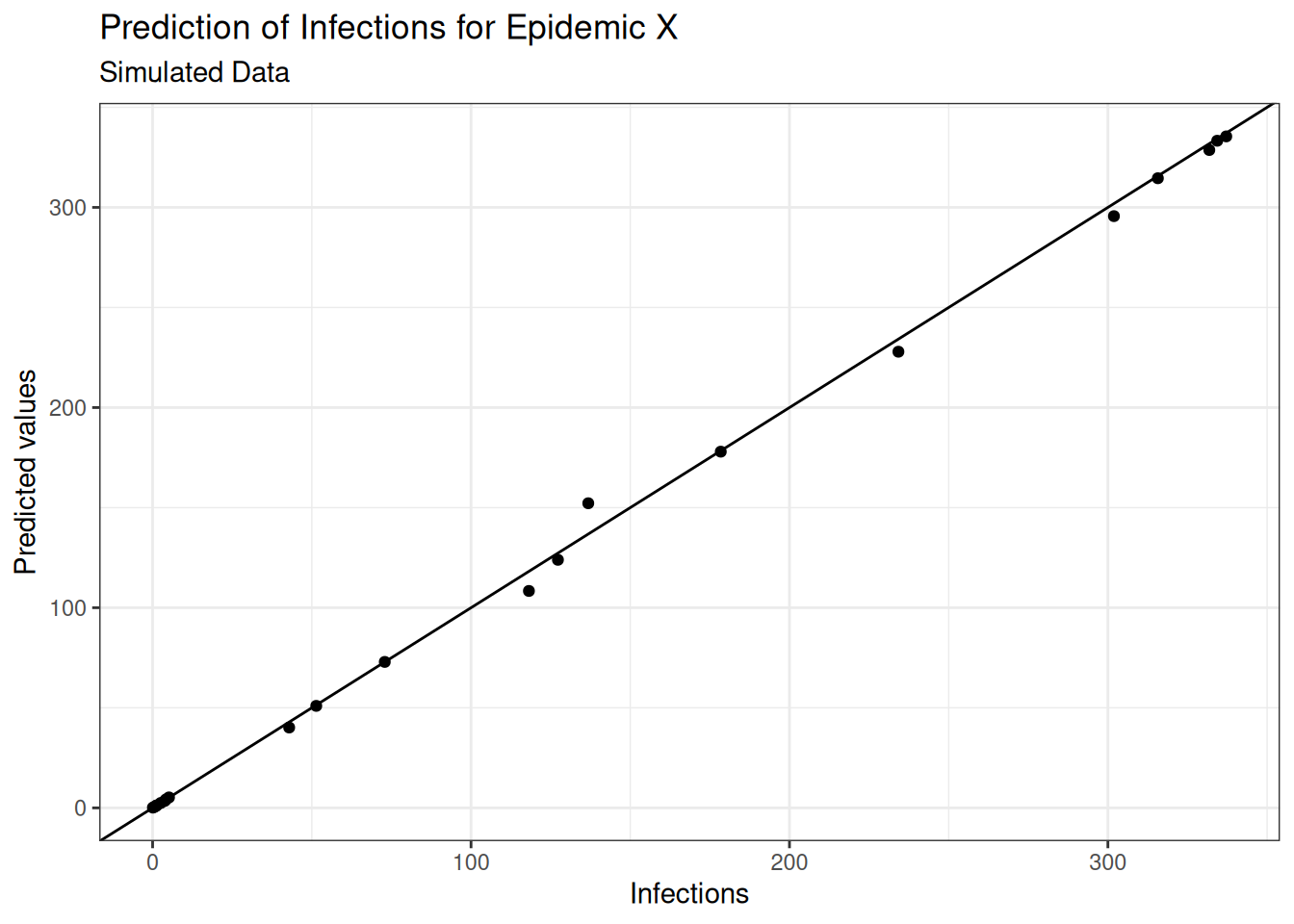
eval_metrics## # A tibble: 3 × 3
## .metric .estimator .estimate
## <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 rmse standard 4.61
## 2 rsq standard 0.999
## 3 mae standard 2.50