N-aray
N-aray transformers
Transformations done on sets of geometries:
- union
- any set of geometries can be combined into a multi-type geometry when they have equal dimensions, or a geometry collection. It’s recommended to use union to combining.
- intersection and difference operate sequentially on all geometries. Example of intersection:
## Geometry set for 7 features
## Geometry type: POLYGON
## Dimension: XY
## Bounding box: xmin: -1 ymin: -1.5 xmax: 2.7 ymax: 2
## CRS: NA
## First 5 geometries:## POLYGON ((-1 1, -0.5 1, -0.5 0, 0.7 0, 0.7 -1, ...## POLYGON ((0.7 -1, 0.7 0, 1 0, 1 -1, 0.7 -1))## POLYGON ((2.7 -1.5, 0.7 -1.5, 0.7 -1, 1 -1, 1 0...## POLYGON ((1 0.5, 1.5 0.5, 1.5 0, 1 0, 1 0.5))## POLYGON ((0.7 0.5, 1 0.5, 1 0, 0.7 0, 0.7 0.5))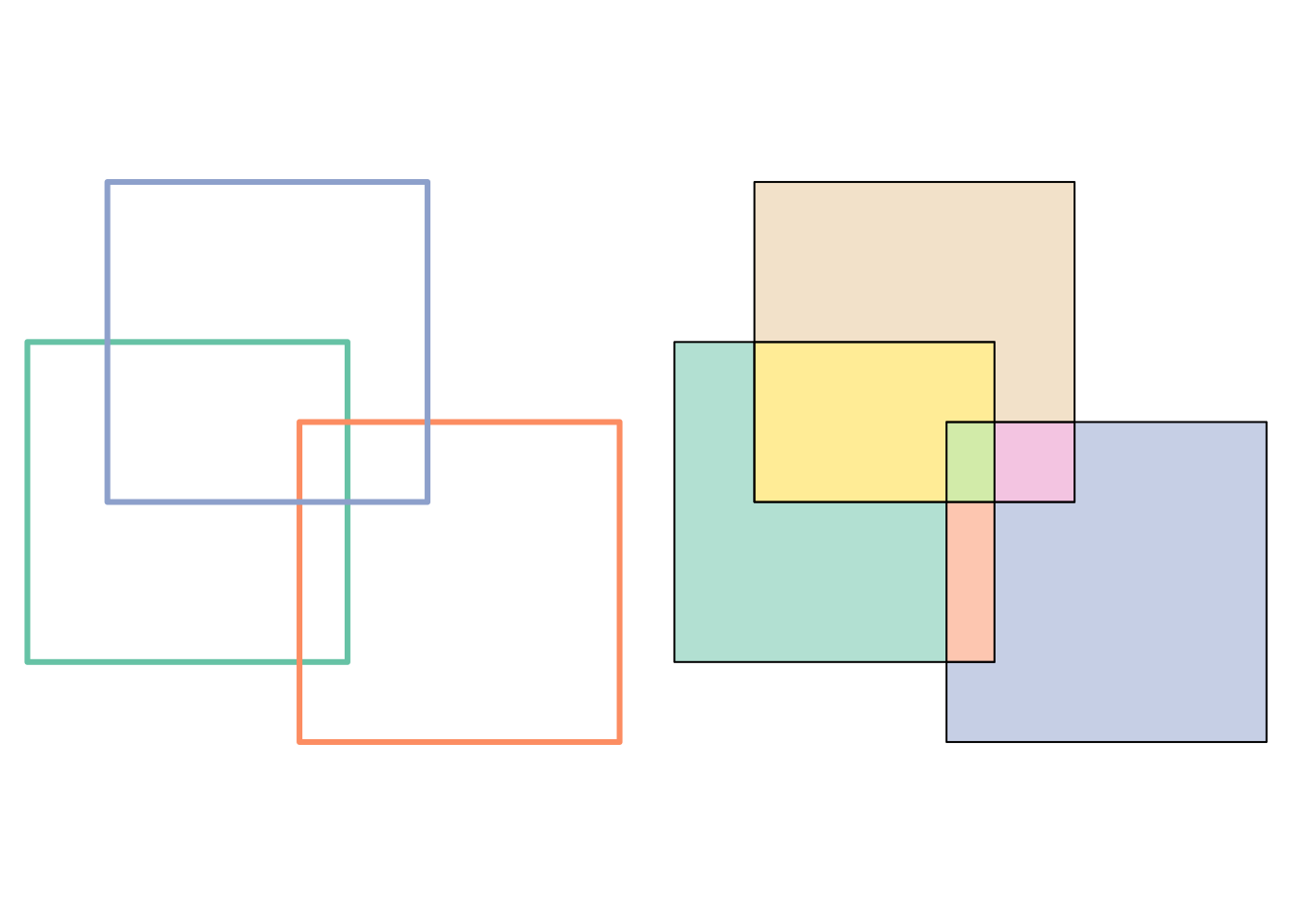
Figure 3.2: Left: three overlapping squares – how do we identify the small box where all three overlap? Right: unique, non-overlapping n-ary intersections