Nonlinear regressions
- not accounting for non-linearity messes up results: range, slope
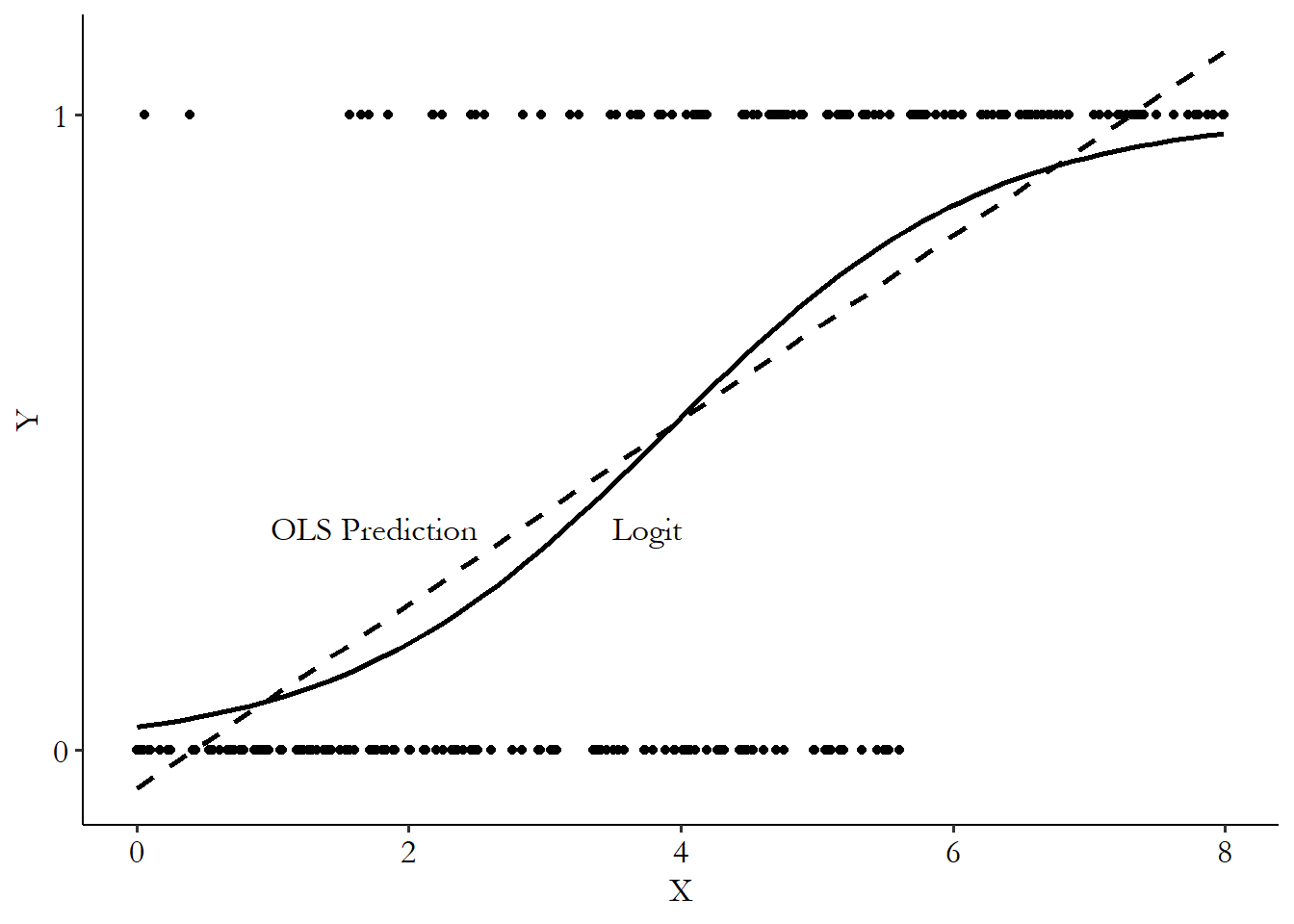
- usually tailored to dependent variable
- binary dependent variables: usually OLS nontheless, but called linear probability model (LPM)
- one way: generalized linear model (GLM): \(Y = F(\beta_0 + \beta_1X)\), where \(F\) is the link function and the inside the index.
good link functions
- take any value from \(-\infty\) to \(\infty\)
- output values between 0 and 1
- input increases –> output increases
- popular functions: logit, probit
Interpretation
- use marginal effects
- \(\frac{\partial Pr(Y = 1)}{\partial X} = \beta_1 Pr(Y = 1) (1- Pr(Y = 1))\)
- but this changes with every \(X\)
- recommendation against marginal effect at the mean
- instead: average marginal effect
