13.5 Hypothesis testing in OLS
author strongly dislikes it, since choice of rejection value is arbitrary and sharp
- Pick a theoretical distribution
- Estimate \(\beta_1\) using OLS in observed data: \(\hat{\beta_1}\)
- Use that theoretical distribution to see how unlikely it would be to get \(\hat{\beta_1}\)
- If it’s super unlikely, that initial value is probably wrong
Alternative: hpyothesis testing
- Pick null hypothesis (typically \(\beta_1 = 0\))
- Pick rejection value \(\alpha\)
- Check probability against rejection value
- Possibly reject null: we think it’s unlikely that the value is 0.
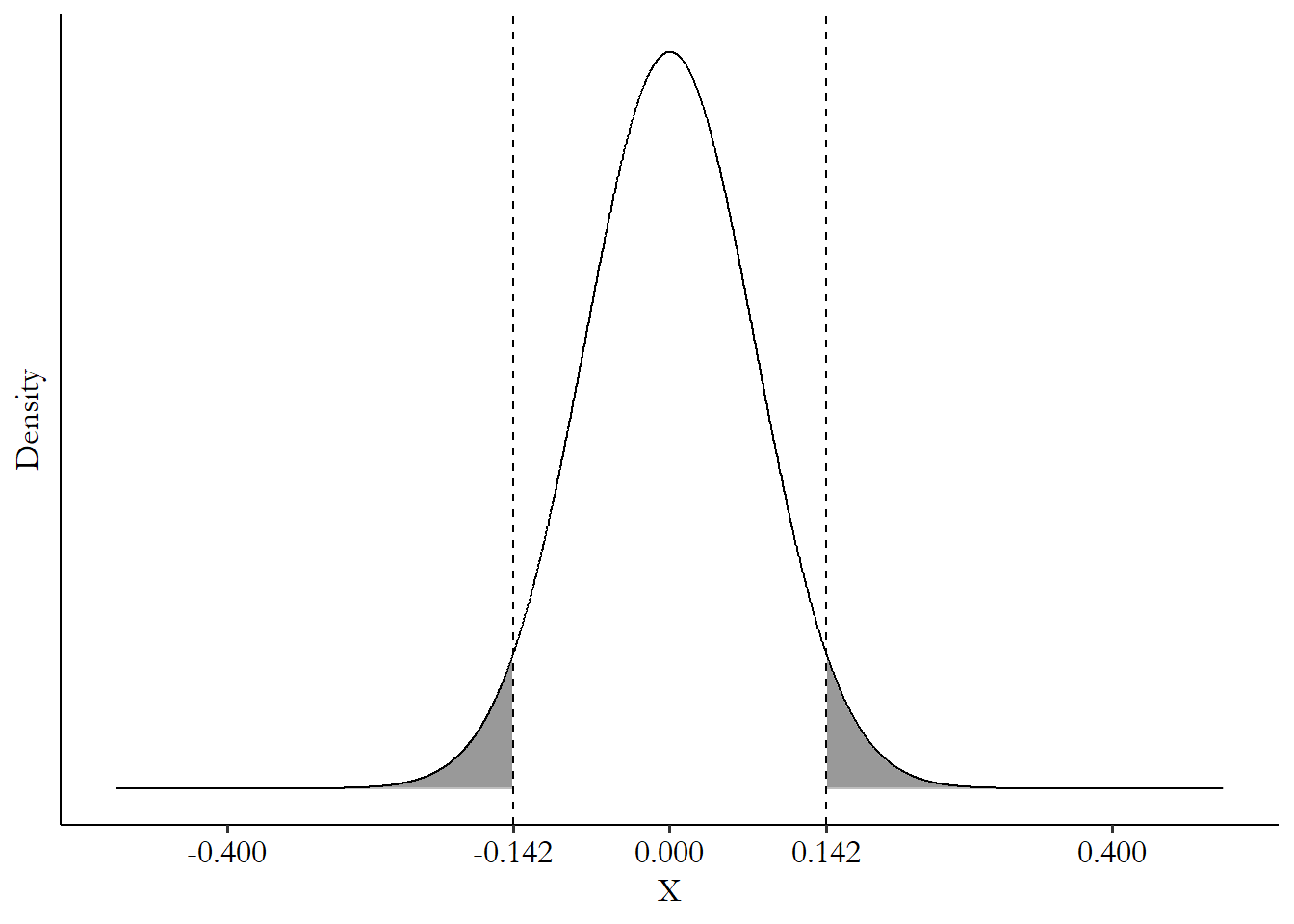
Type I error rate (“false positive rate”): rejection of something that’s true
Type II error rate (“false negative rate”): not rejecting something that’s false
p-value: double percentile (2-sided test)
t-statistic: \(\frac{\hat{\beta_1}}{se(\hat{\beta_1})}\) to use with standard normal distribution