14.3 Performing Kriging in R
To perform Kriging in R, you can use the gstat package, which provides functions for geostatistical analysis. The gstat package allows you to create a variogram model, fit the model to the data, and use the model to interpolate values at unobserved locations.
14.3.1 Example: Simple Kriging
In this example, we will perform simple Kriging on a dataset of air quality measurements. We will estimate the air quality at unobserved locations based on the measurements at nearby monitoring stations.
Step 1: Load the air quality data and create a variogram model.
library(sp)
# Load the air quality data
data(meuse)
coordinates(meuse) <- c("x", "y")
meuse%>%
as_data_frame()%>%
select(x,y,zinc)%>%
head()## # A tibble: 6 × 3
## x y zinc
## <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 181072 333611 1022
## 2 181025 333558 1141
## 3 181165 333537 640
## 4 181298 333484 257
## 5 181307 333330 269
## 6 181390 333260 281Step 2: Visualize the data.
meuse%>%
as_data_frame()%>%
select(x,y,zinc)%>%
ggplot(aes(x,y,color=zinc))+
geom_point()+
scale_color_viridis_c()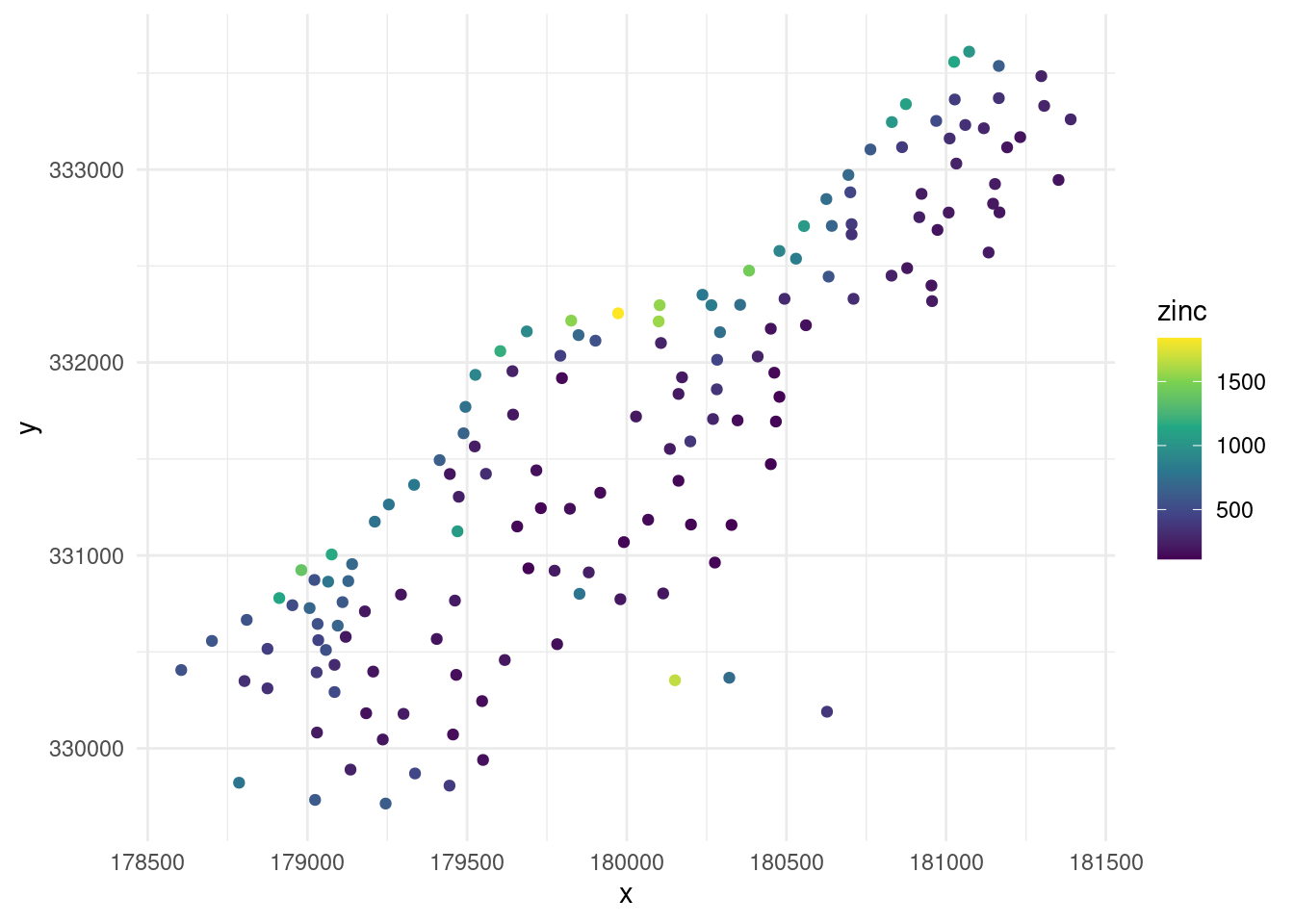
What we need is a grid of points where we want to predict the zinc concentration.
data(meuse.grid)
meuse.grid %>%
as_data_frame()%>%
select(x,y)%>%
ggplot(aes(x,y))+
geom_point(shape=".")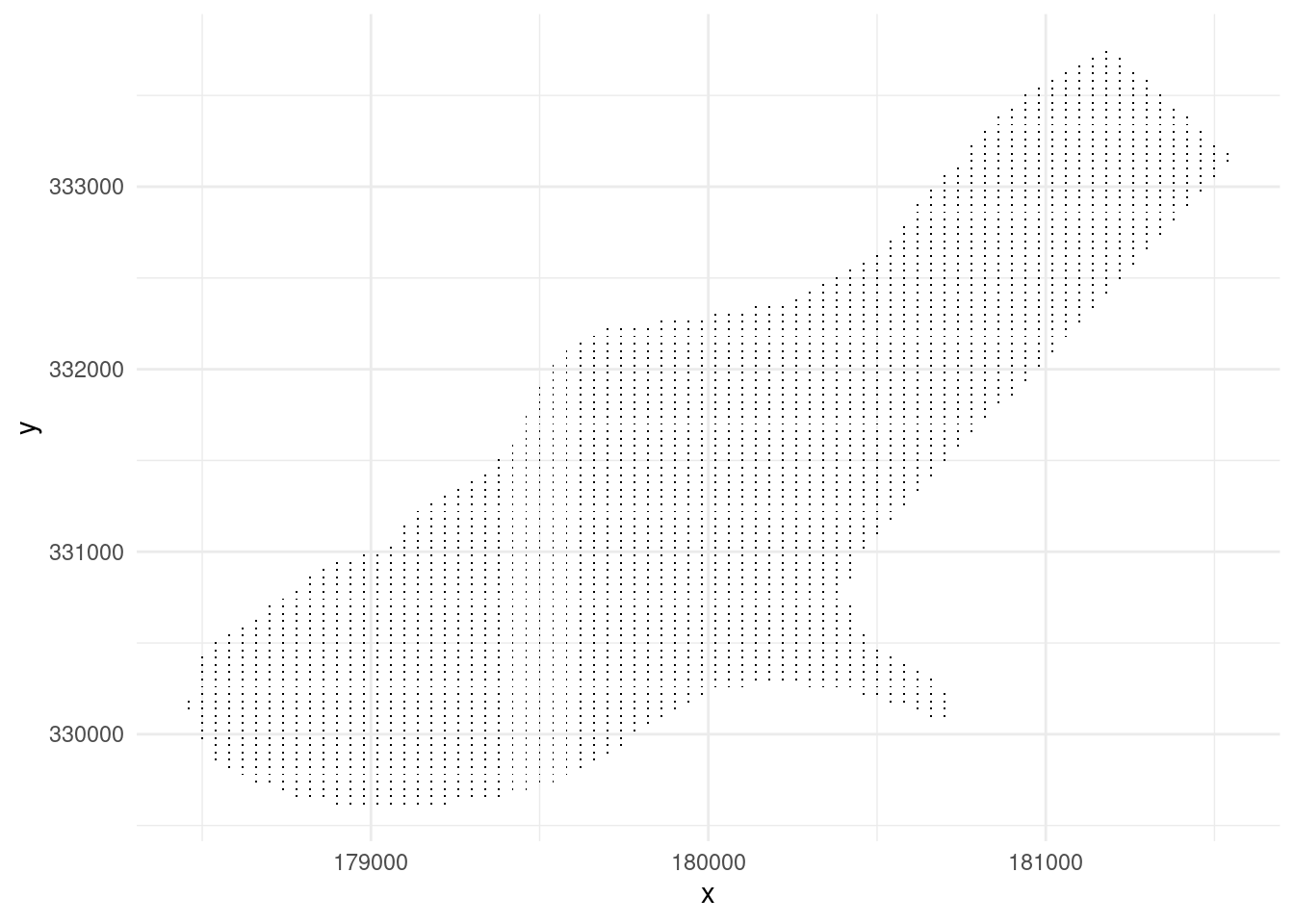
zinc_data <- meuse%>%
as_data_frame()%>%
select(x,y,zinc)
grid_data <- meuse.grid %>%
as_data_frame()%>%
select(x,y)
ggplot()+
geom_point(data=grid_data,aes(x,y),shape=".")+
geom_point(data=zinc_data,aes(x,y,color=zinc))+
scale_color_viridis_c()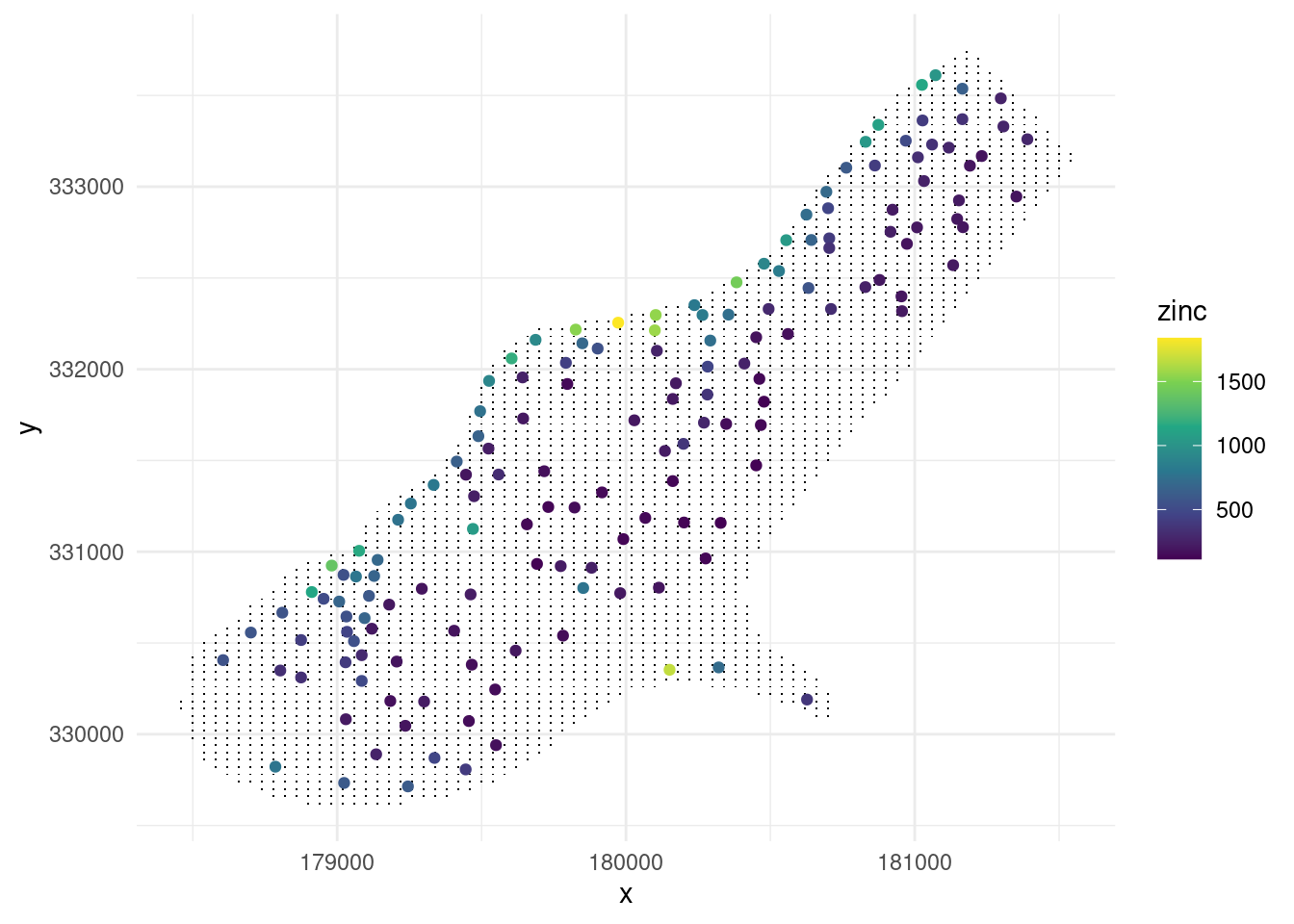
14.3.2 Variogram Model
We perform a Variogram analysis to understand the spatial correlation of the zinc concentration in the dataset.
Formula: \(V(h) = \frac{1}{2N(h)} \sum_{i=1}^{N(h)} (Z(s_i) - Z(s_i + h))^2\)
where \(V(h)\) is the semivariance at lag distance \(h\), \(N(h)\) is the number of pairs of observations at lag distance \(h\), \(Z(s_i)\) is the value of the variable at location \(s_i\), and \(Z(s_i + h)\) is the value of the variable at location \(s_i\) plus lag distance \(h\).
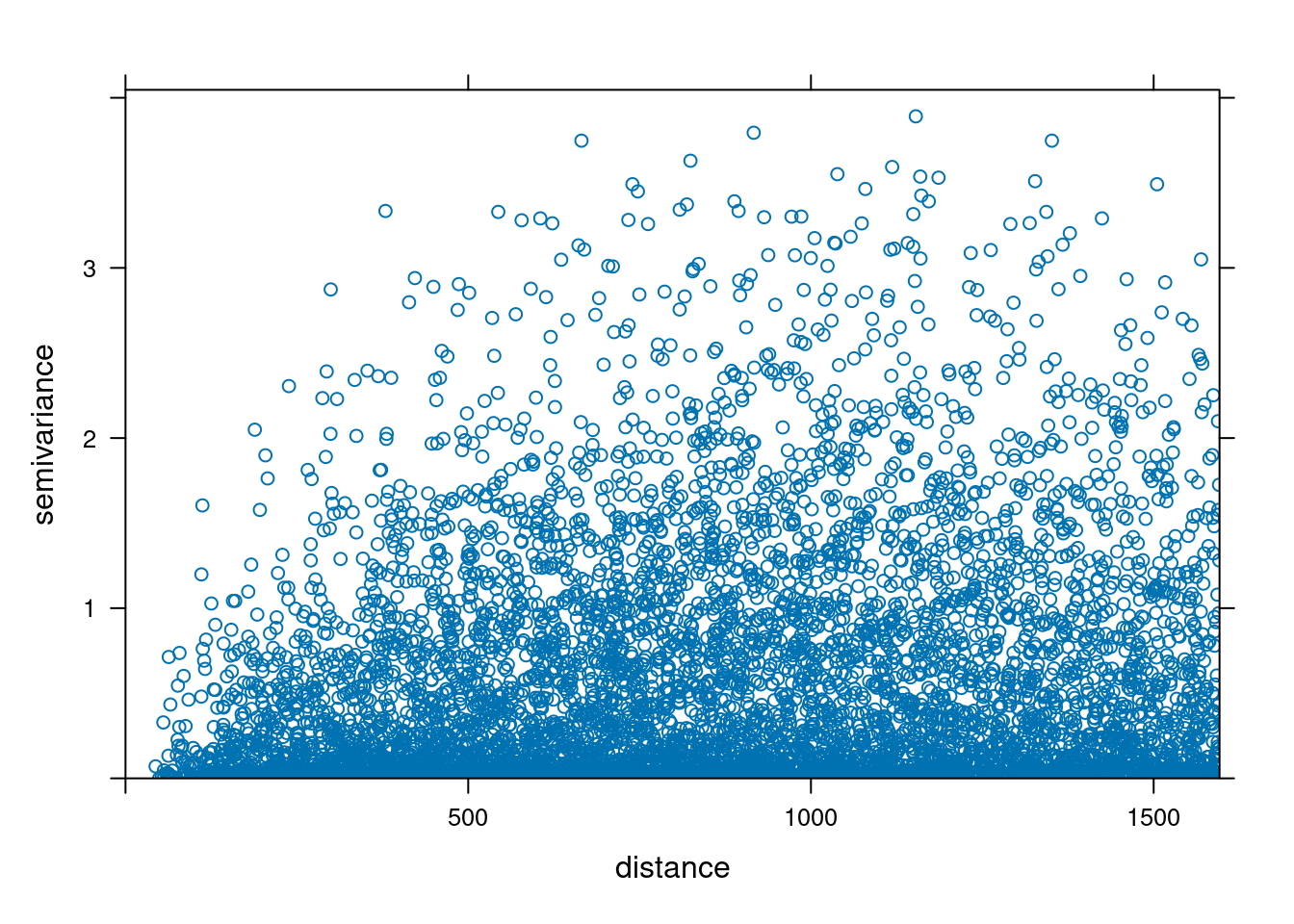
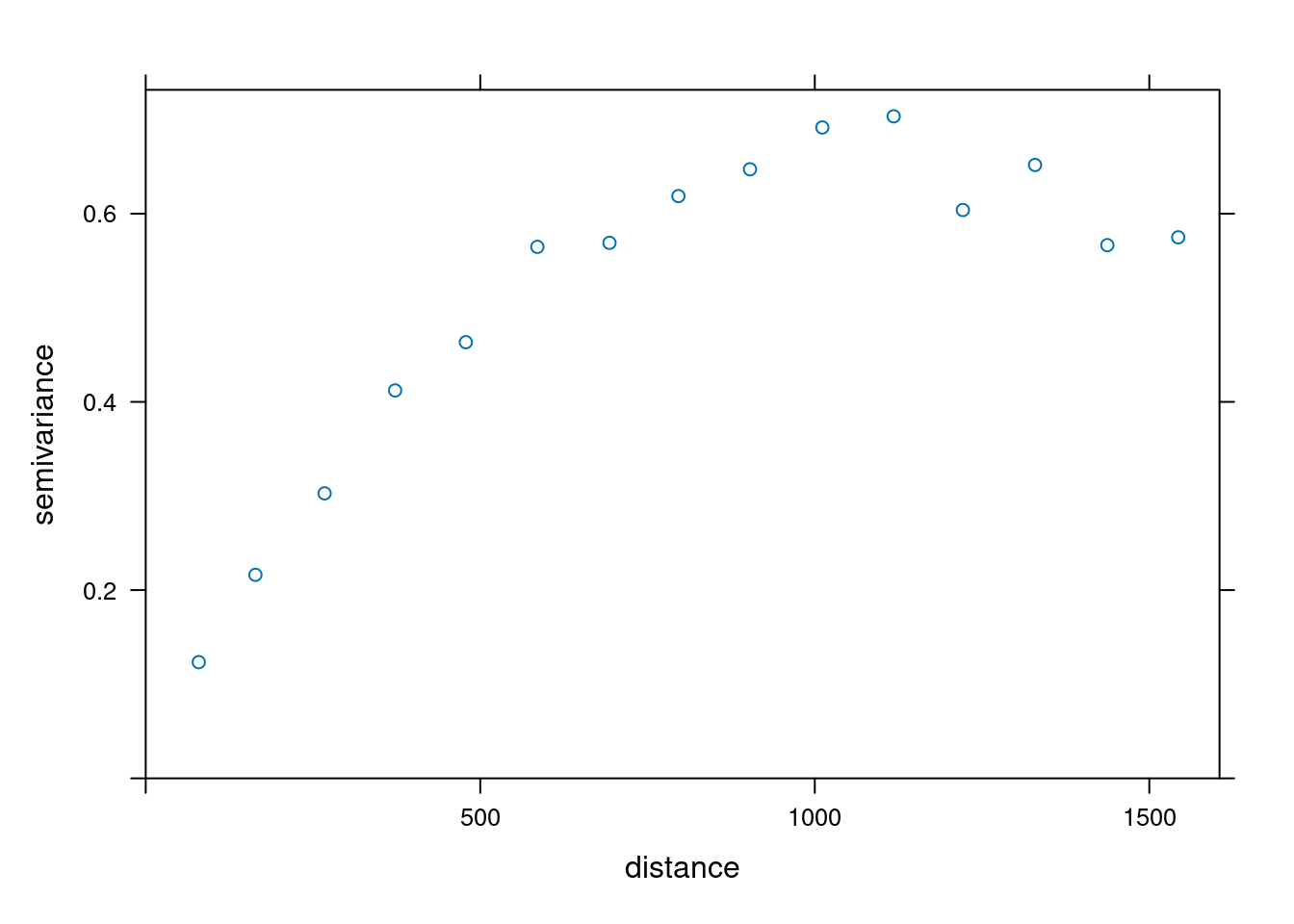
# Fit the variogram model
fv <- fit.variogram(object = v,
model = vgm(psill = 0.5,
model = "Sph",
range = 900,
nugget = 0.1))
plot(v,fv)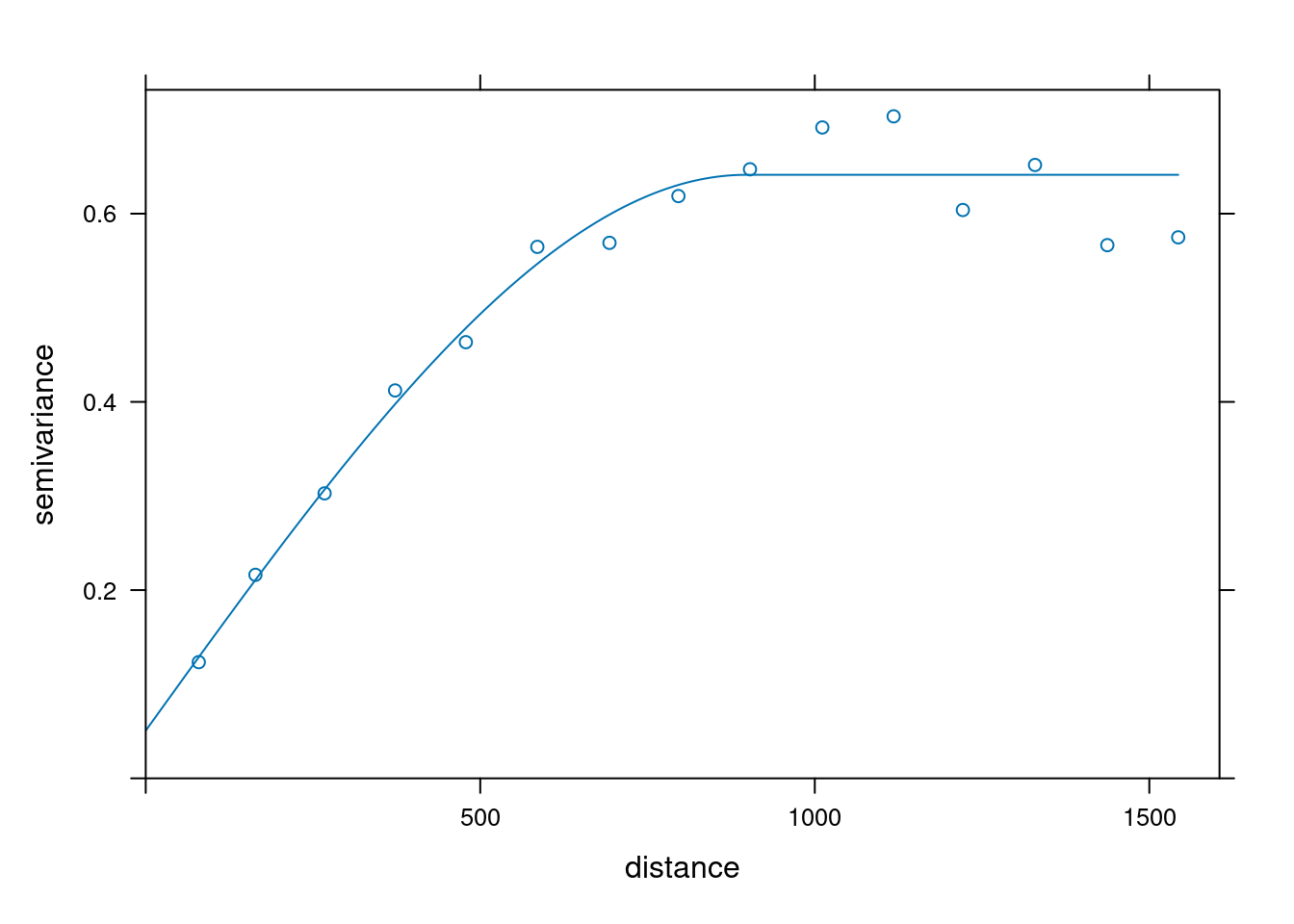
14.3.3 Perform Simple Kriging
gstat function to compute the Kriging predictions:
`?gstat`
library(sf)
data(meuse)
data(meuse.grid)
meuse <- st_as_sf(meuse,
coords = c("x", "y"),
crs = 28992)
meuse.grid <- st_as_sf(meuse.grid,
coords = c("x", "y"),
crs = 28992)
fv <- fit.variogram(object = v,
model = vgm(psill = 0.5,
model = "Sph",
range = 900,
nugget = 0.1))
fv## model psill range
## 1 Nug 0.05066017 0.0000
## 2 Sph 0.59060556 897.0044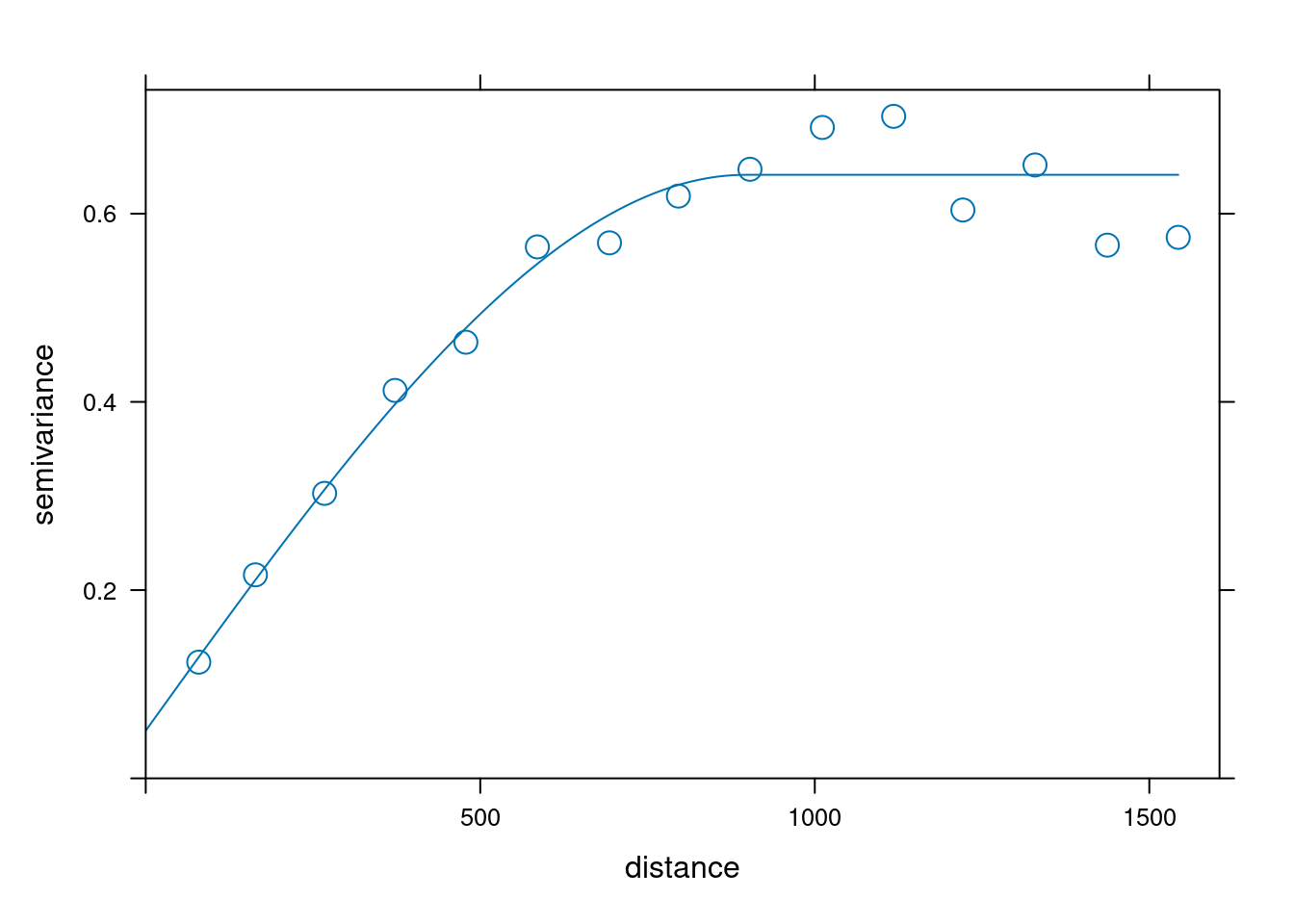
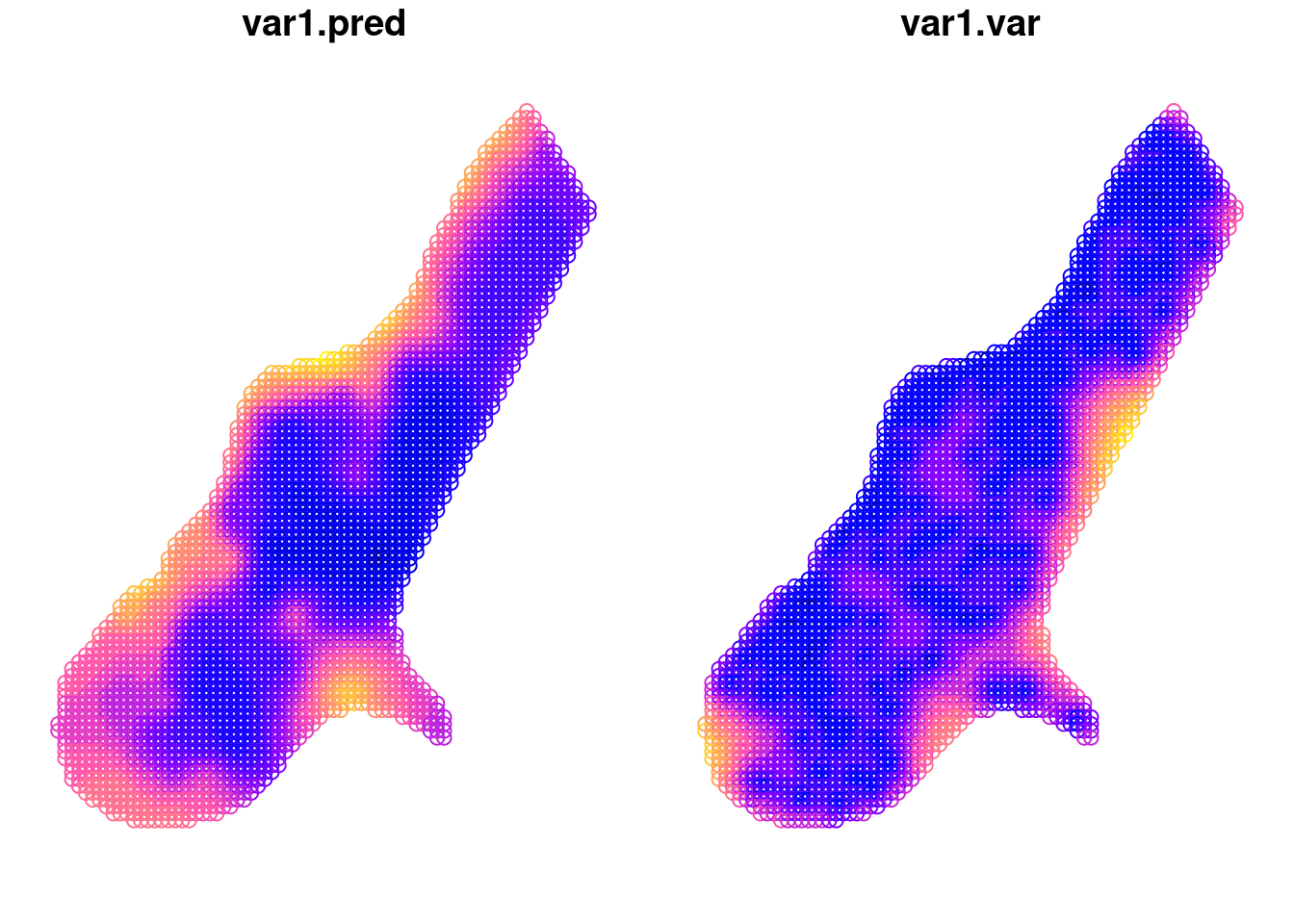
## [using ordinary kriging]ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = kpred,
aes(color = var1.pred)) +
# geom_sf(data = meuse) +
viridis::scale_color_viridis(name = "log(zinc)")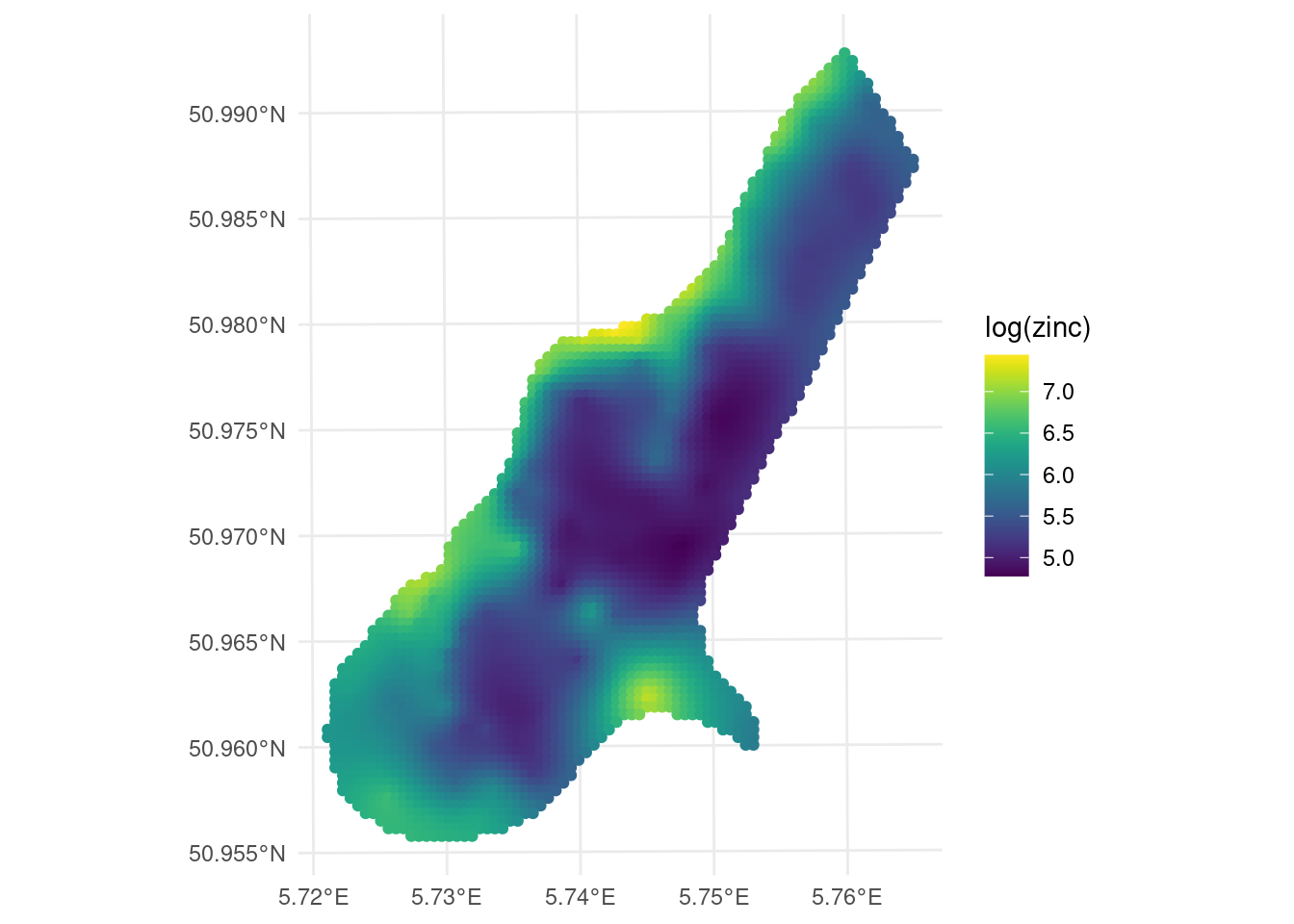
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = kpred,
aes(color = var1.var)) +
geom_sf(data = meuse) +
viridis::scale_color_viridis(name = "variance") 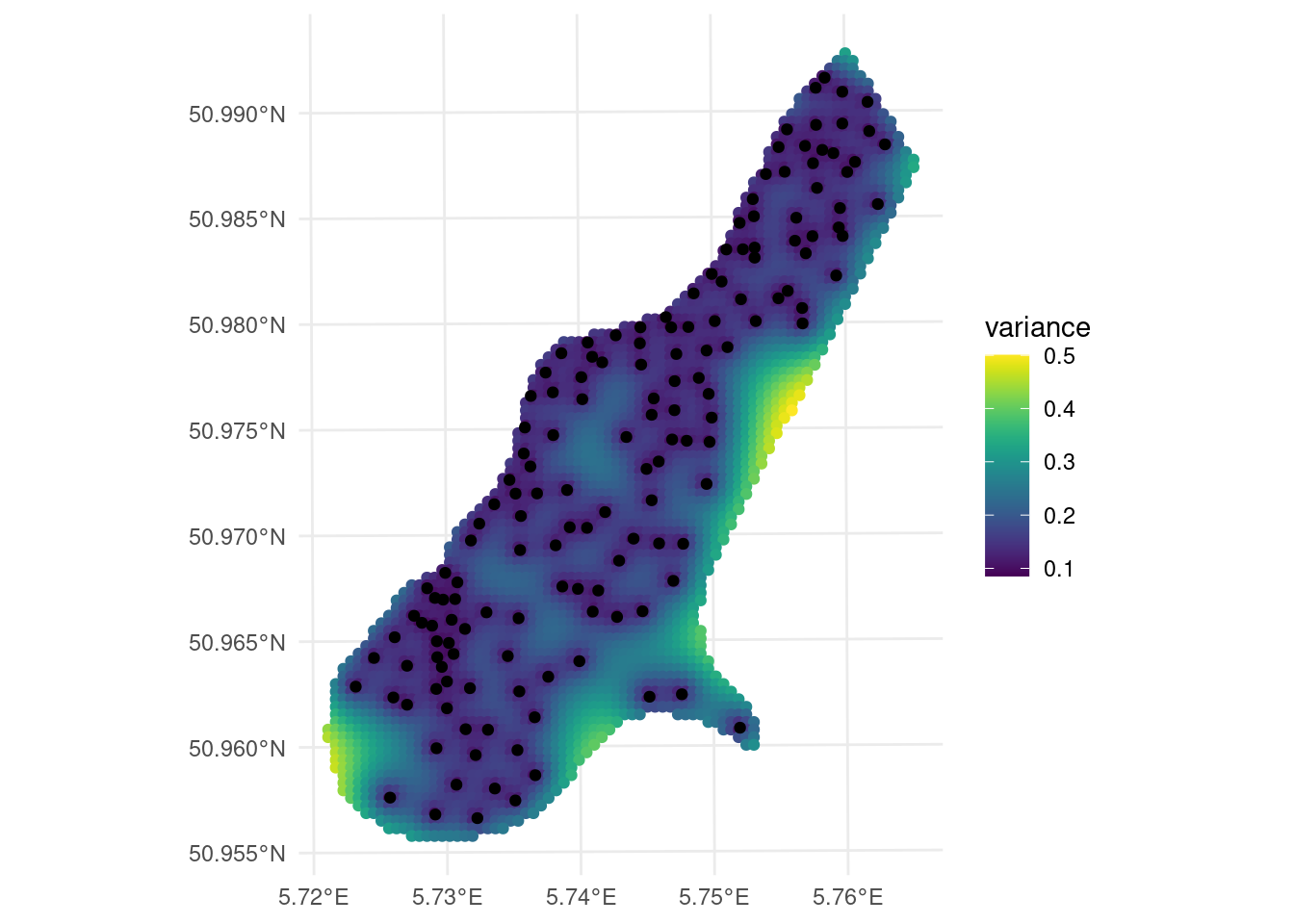
## [using ordinary kriging]