7. Statistical Prediction with Neural Networks
Learning objectives
Neural nets fundamentals
ANNs
- An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is machine learning model designed to find nonlinear patterns in data.
- It is a set of connected units aggregated into layers.
- Each neuron receives signals (real numbers) from its connected neurons and process its inputs through an activation function.
- ANNs are trained to minimize the difference between the predicted output and the actual target values in a given dataset.
- Training requires adjusting function parameters
- Neural Networks and Deep Learning - Chapter 1
Network architecture
The number of neurons in the input/output layers is related to their application.
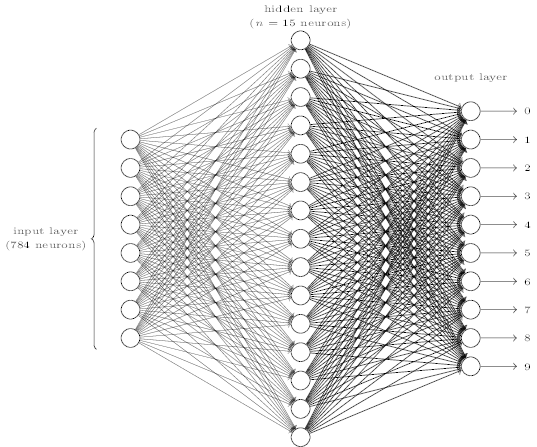
1neuron input with1neuron output: Ex. drug dosage and binary response. Like linear regressionNneuron inputs,Mneuron outputs: N number of features. M number of categories in classification.* Example: classification of images into digits. 28x28 input neuron from a 28x28px image and 10 output networks for digits.
The Perceptron
- A type of artificial neuron developed in the 1950s and the 1960s
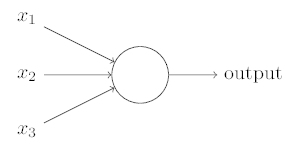
It takes several binary inputs \(x_1,x_2,x_3\) and produces a single binary output
Each input has an associated weight \(w_1,w_2,w_3\) indicating the importance of its input to the output.
To calculate the output: \[ output = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} 0 & \text{if } \sum_jw_jx_j \leq \text{threshold}\\ 1 & \text{if } \sum_jw_jx_j \geq \text{threshold} \\ \end{array} \right. \]
A network of perceptrons could weigh up evidence and make decisions, like computing logical functions with binary operations such as AND, OR or NAND gates.
From binary to sigmoid functions

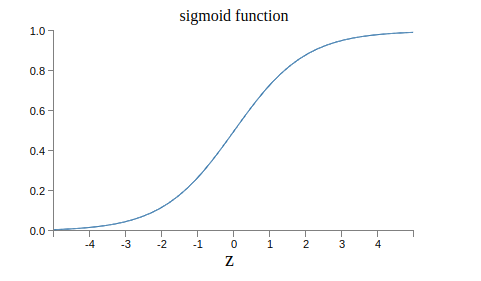
The output is defined by the sigmoid function:
\[\sigma(z)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-z}}\] \[\sigma(w\cdot x+b)=\frac{1}{1+exp(-\sum_jw_jx_j-b)}\]
Inputs \(x_j\) and single output in the \([0,1]\) range.
Weights, \(w_j\) tell us how important each input is.
Bias \(b\) tell us how high the sum needs to be to activate the neuron.
Backpropagation
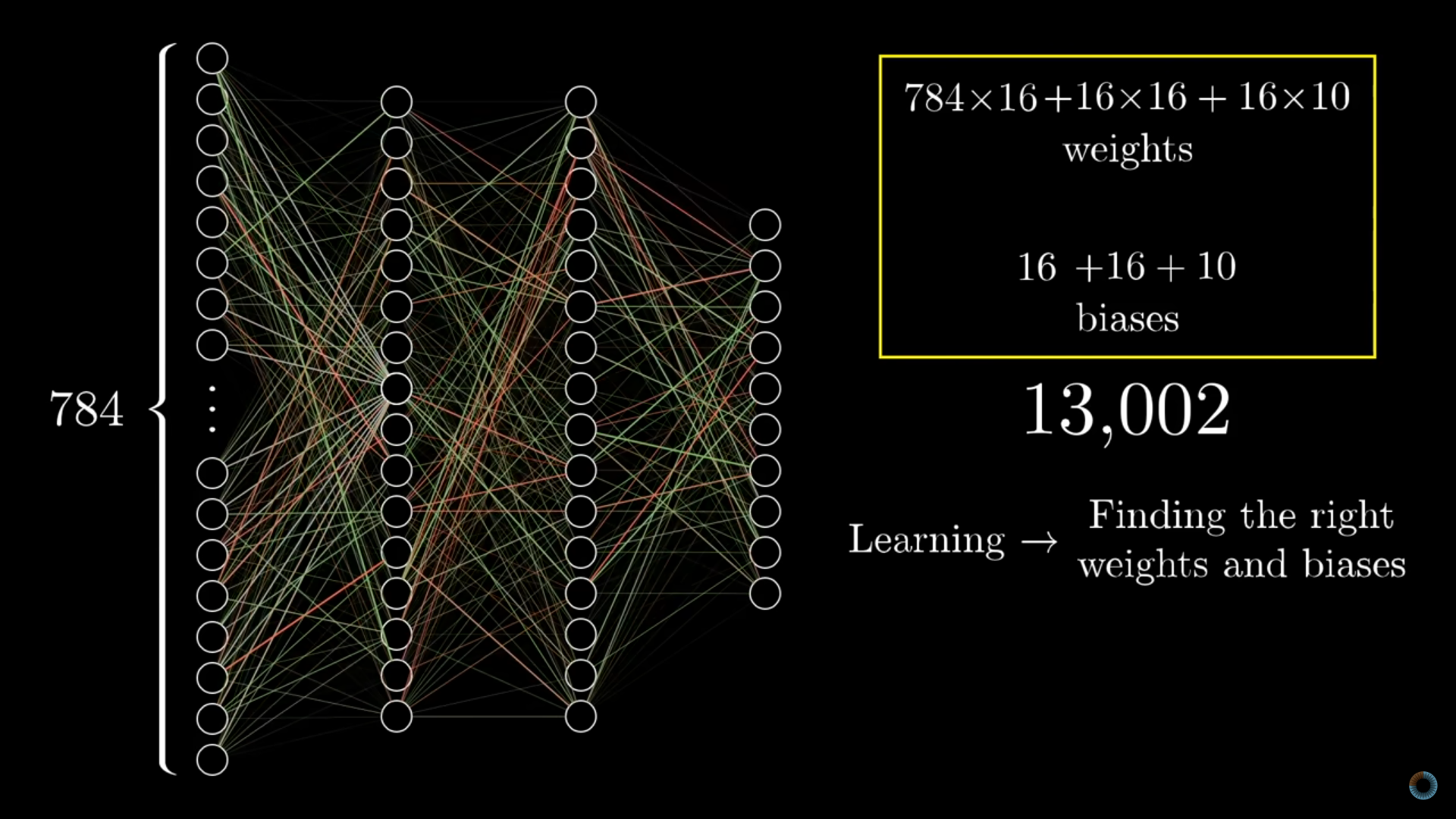
ANN learning
From: But what is a neural network? | Deep learning chapter 1
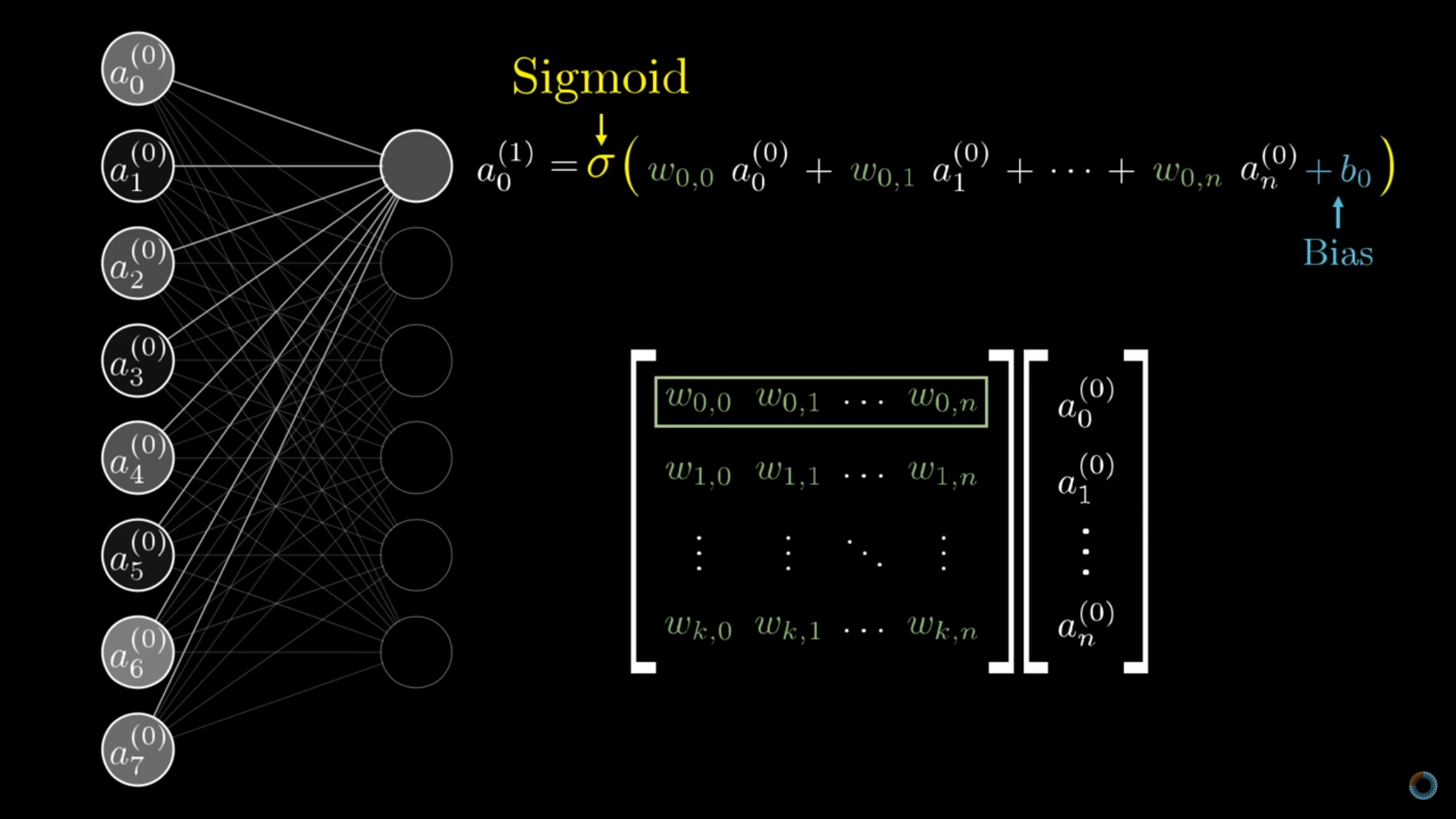 From: But what is a neural network? | Deep learning chapter 1 Matrix operations
From: But what is a neural network? | Deep learning chapter 1 Matrix operations
Cost function
Goal: find weights and biases so that the output of the network approximates \(f(x)\) for all training inputs.
To evaluate how well we’re achieving this goal, we define a cost function, also referred to as loss or objective function.
Common one: mean squared error
\[ C(w,b) = \frac{1}{2n}\sum_x ||y(x)-a||^2 \] We want \(C(w,b)\approx 0\), so we want to minimize the function
Gradient descent
In \(x,y\), the slope of the derivative is the rate of change of a function at a specific point.
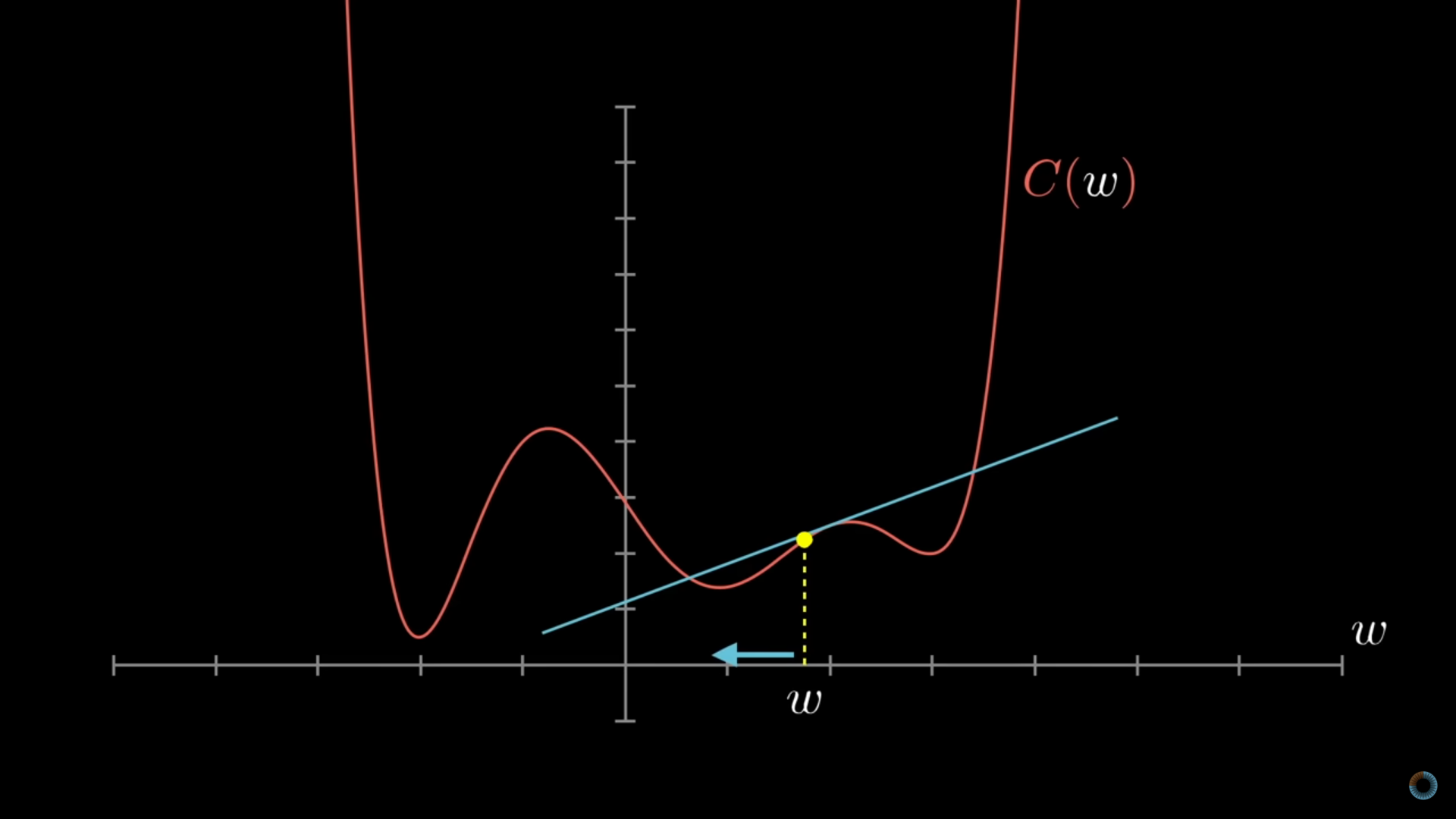
Gradient descend
Gradient descend calculation
With partial derivatives using the chain rule (from Leibniz)
A very simple example:
Algorithm
- Inputs are propagated from the input to the output layer.
- The network error is calculated.
- The error is propagated from the output layer to the input layer - backpropagation.
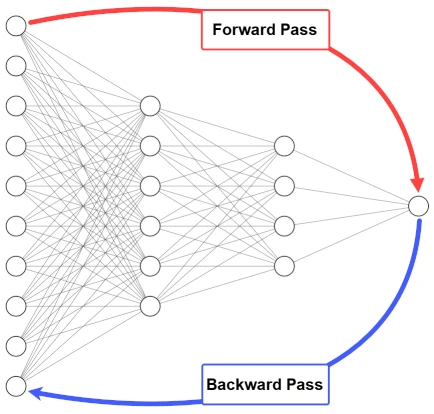
We get the derivatives of the cost function with respect to each individual \(w\) and \(b\) and update them according to a learning rate.
We repeat until the change is really small or we reach some other condition.
Again

Training Algorithm
Backpropagation implementation
Artificial Neural Networks
What do we need?
- A network structure with input, output and h hidden layers.
- One weight value per link (neuron-neuron connection).
- One bias value per neuron.
- An activation function for the neurons, usually ReLU or sigmoid.
- A cost function to minimize during training and to tune weight and biases values.
- A training algorithm more like stochastic gradient descent.