Enterprise Server Management
Learning objectives
- Simplyfing Complexity Using Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- How to Scale and Stabilize Workloads in Enterprise-Level Organisations
- Facilitating Enterprise Workloads Management with Kubernetes
Simplyfing Complexity Using Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Servers should be cattle, not pets.
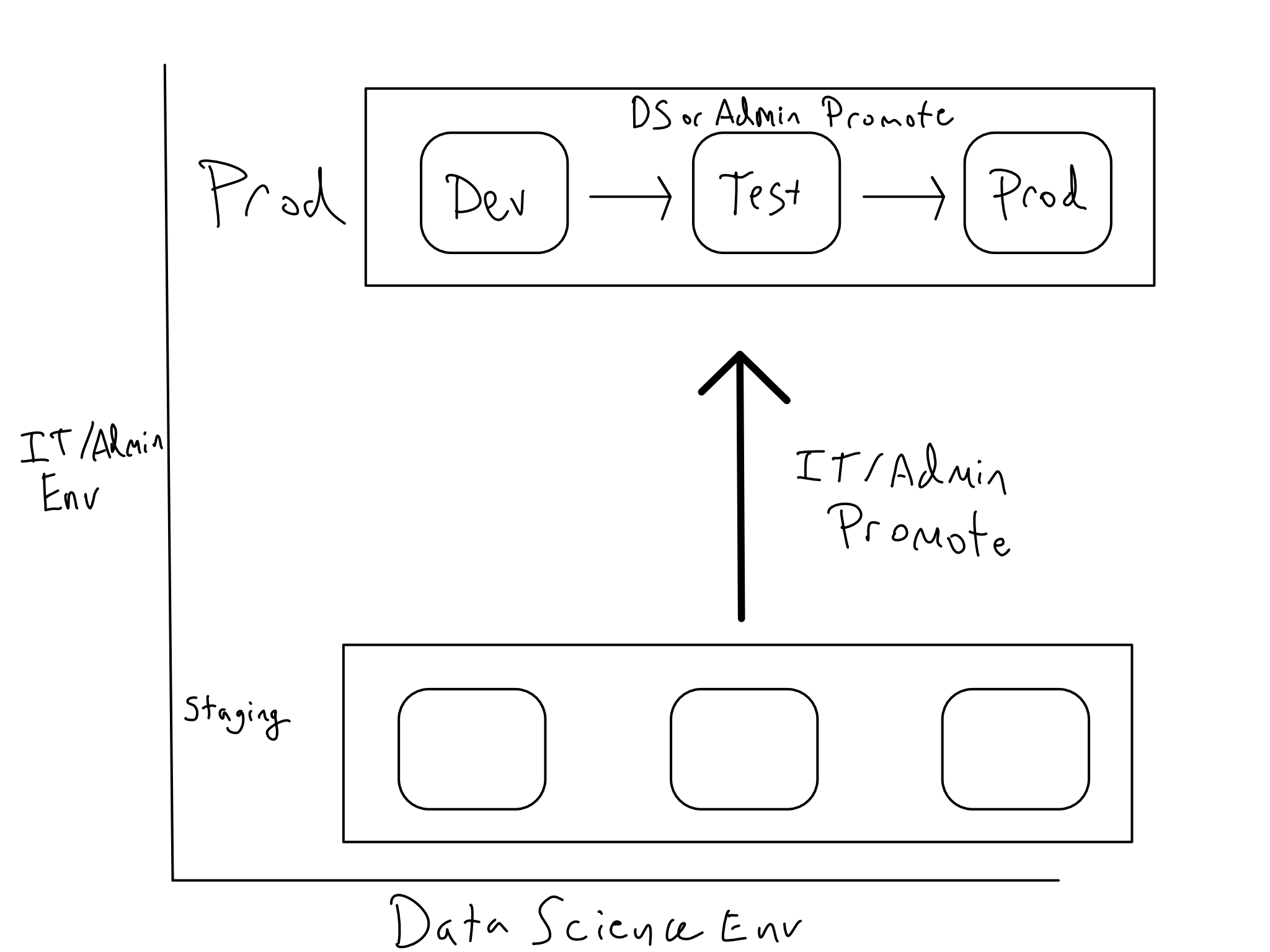
Alex recommended a two-dimensional Dev/Test/Prod setup
![]()
IT/Admin group make changes to the platform in a staging environment.
Data scientists are never granted access to the staging environments and must complete all of their work in the IT/Admin production environment.
The ideal approach to migrate servers and apps from staging to production is to use IaC and CI/CD to ensure that code changes always make it into production at the proper time.
How to Scale and Stabilize Workloads in Enterprise-Level Organisations
Vertical Scaling Limitations and Horizontal Scaling to the rescue
- Before attempting horizontal scaling, it is usually always good to exhaust the portion of vertical scaling where costs climb linearly with computation.
High Availability is achieved by
Using Load balancers in Horizontal scaling
Imagine a restaurant with one chef that is trying to serve meals to a hundred customers at once.
The chef can only cook one meal at a time, so the customers are getting frustrated with long wait times and some of them are leaving.This is because the chef is overloaded and cannot handle the intense workload.
Now, imagine the restaurant hires three more chefs, all with the same skills and equipment as the first chef. The restaurant invests in a system where each chef has a buzzer that goes off when there are new orders waiting for them. The buzzer ensures that each chef knows exactly when they need to start cooking a new meal, and they do not get overwhelmed by too many orders at once.
In this analogy, the chefs represent servers or clusters, and the buzzer represents a load balancer.
Maintaining a backup of the load balancer and the database/NAS.
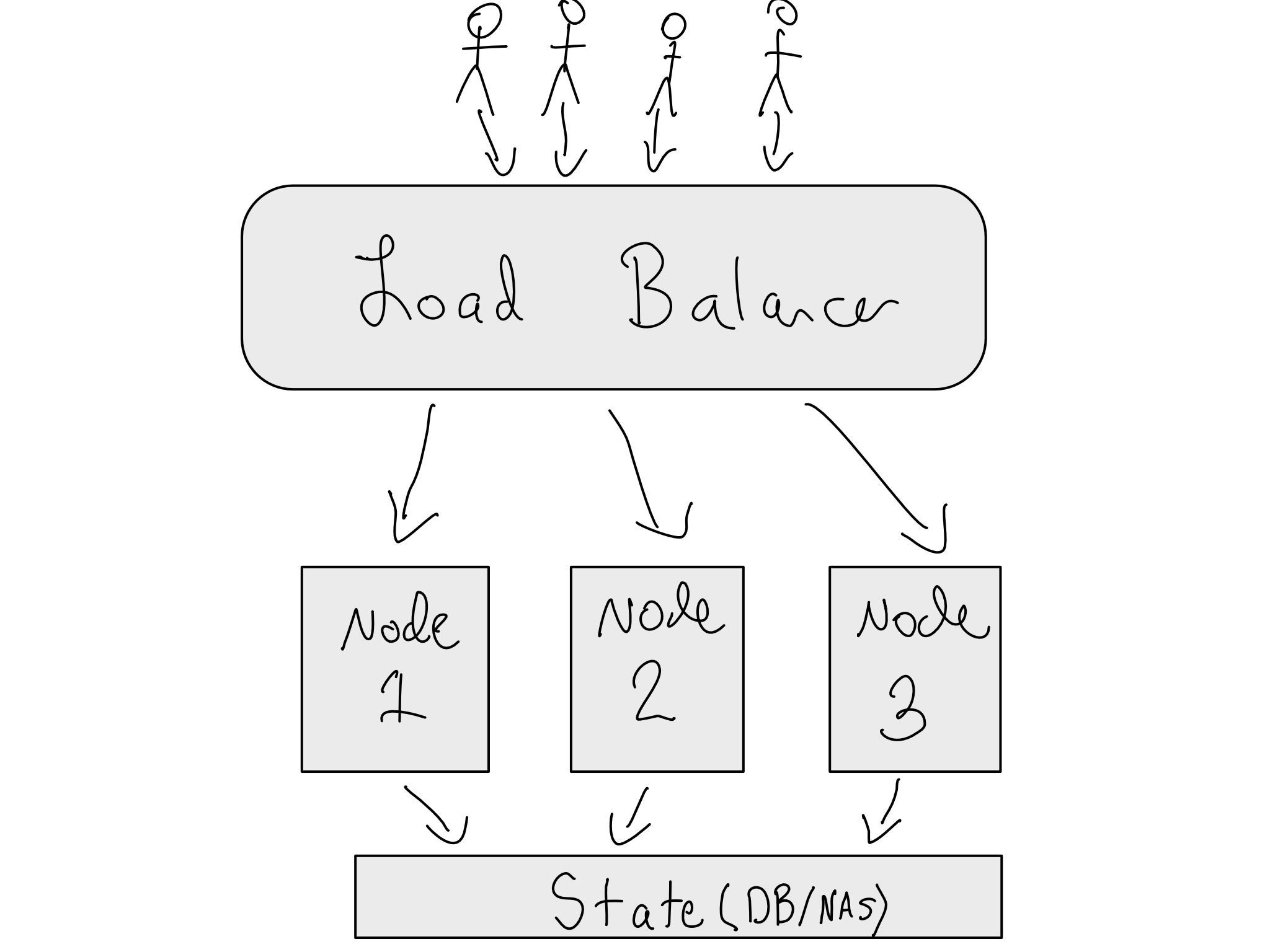
- Adding Autoscaling (i.e. you save money when traffic is low)
- Many autoscaling frameworks these days assume that applications are mostly stateless.
Facilitating Enterprise Workloads Management with Kubernetes
Kubernetes solves all three of the key enterprise IT/Admin challenges with running servers.
Increasing the processing power of your cluster is usually as simple as a few mouse clicks. On the other side, this makes it risky from a cost perspective.
Helm is the standard tool for defining what’s running in the cluster.
Instead of the ten steps required in a typical server-based deployment. There are just three steps for Kubernetes.
What are the biggest strengths of Kubernetes as a scaling tool? What are some drawbacks?
Strengths:
Automatic Load Balancing
Horizontal Scaling
Infrastructure Agnosticism
Drawbacks:
Managing and maintaining a Kubernetes cluster can be complex and time-consuming and really requires a highly competent Kubernetes admin
Networking in Kubernetes can also be quite complicated.