Getting Comfortable on the Command Line
Learning objectives
- Set up and customize your machine’s command line
- Access a server via SSH (secure socket shell)
Command Line
Why use Command Line?
- On a server, administrative interaction is via the command line
- Many tasks are quicker and easier
Admin via GUI
In some organizations, server admin tasks are done via a graphical tool, but this is a red flag.
It means that the organization is either trying to find relatively low-paid (and probably low-skilled) admins or are using a graphical tool to limit what IT/Admins can do. Either way, it’s going to be harder to get things done.
Getting the command line you want
The terminal is the GUI where you’ll type in commands
RStudio, Positron, and VS Code have built-in terminals
Author recommends
iTerm2for MacOSThe shell takes the commands you type and runs them
Matches the commands you type to actual programs on your system, e.g.
Rscript,positron,code,git, etc.MacOS and Linux have bash and zsh, while Windows comes with Command Shell (
cmd) and the PowerShell. Also, git bash on Windows
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is another option
Configuration management
Customization tools for window/tab behavior and text theme/plugins:
- MacOS:
PreztoorOhMyZsh. Three places to configure:- iTerm2 preferences
- the zsh configuration file
.zshrc
- Prezto configuration file
.zpreztorc
- iTerm2 preferences
- Author recommends looking into Git plugins, auto-completion and command history search functionality
- Windows:
Oh My Poshfor PowerShell
Text editors
- IDE (RStudio, Positron, o VS Code)
- Standalone: Sublime or Notepad++ (Windows only)
SSH
Secure server connections with SSH
- Remotely accessing a server from the command line on your machine
- SSH (Secure Socket Shell) is a tool for making a secure connection to another computer over an unsecured network
- SSH requires invoking the
sshcommand line interface from a local host (your computer) with a username and the remote host’s (server’s) address.
For example, connecting to the server at server.example.com as the user alex would look like:
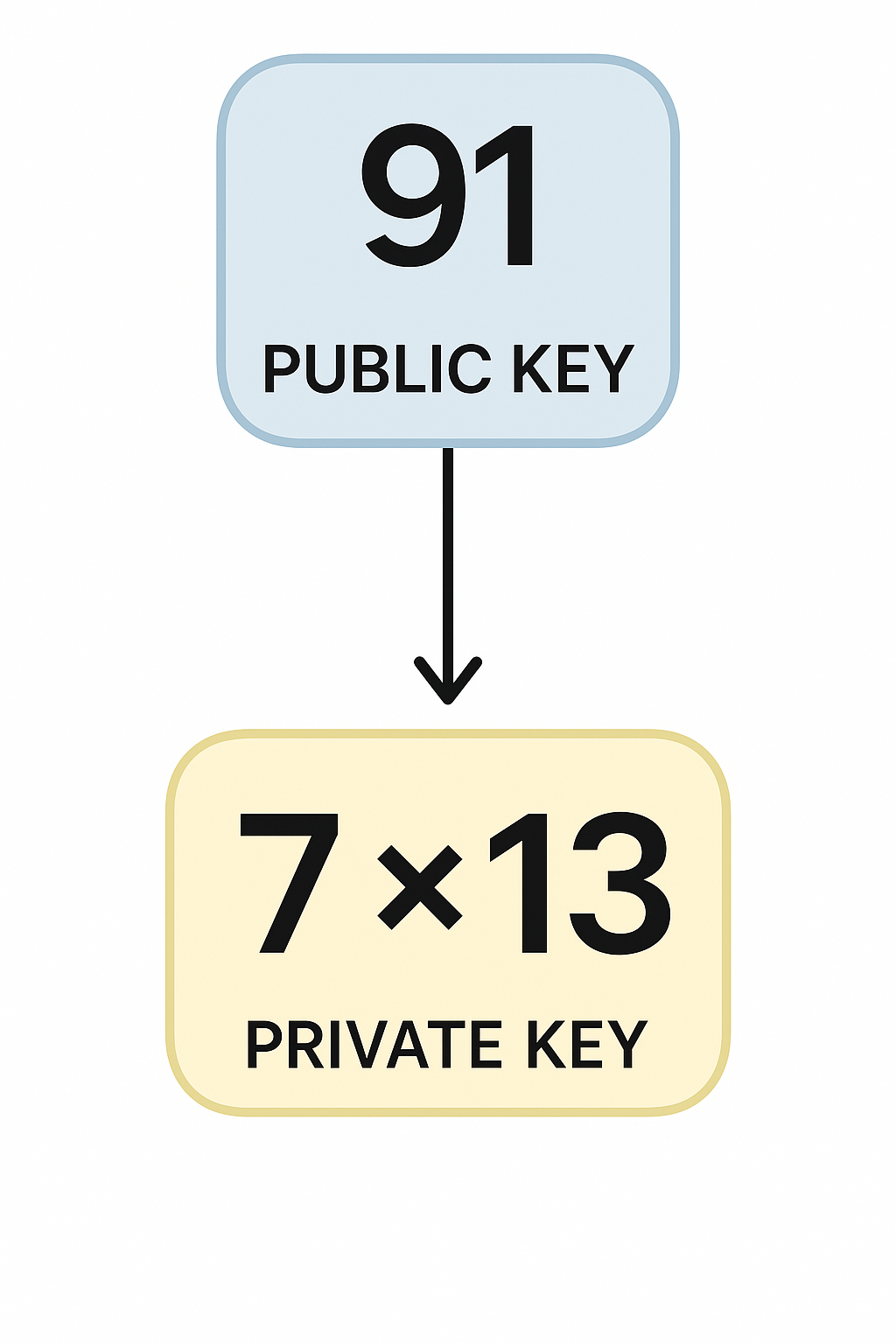
Understanding SSH Keys
- Configure your SSH keypair (public key and private key)
- Public key: Register anywhere you’re trying to SSH into.
- Private key: Secret
- Public key is the lock and private key is the key
Public Key Cryptography
- Public key cryptography is the underlying technology
- Never move the private key from the computer where it was created and never share it
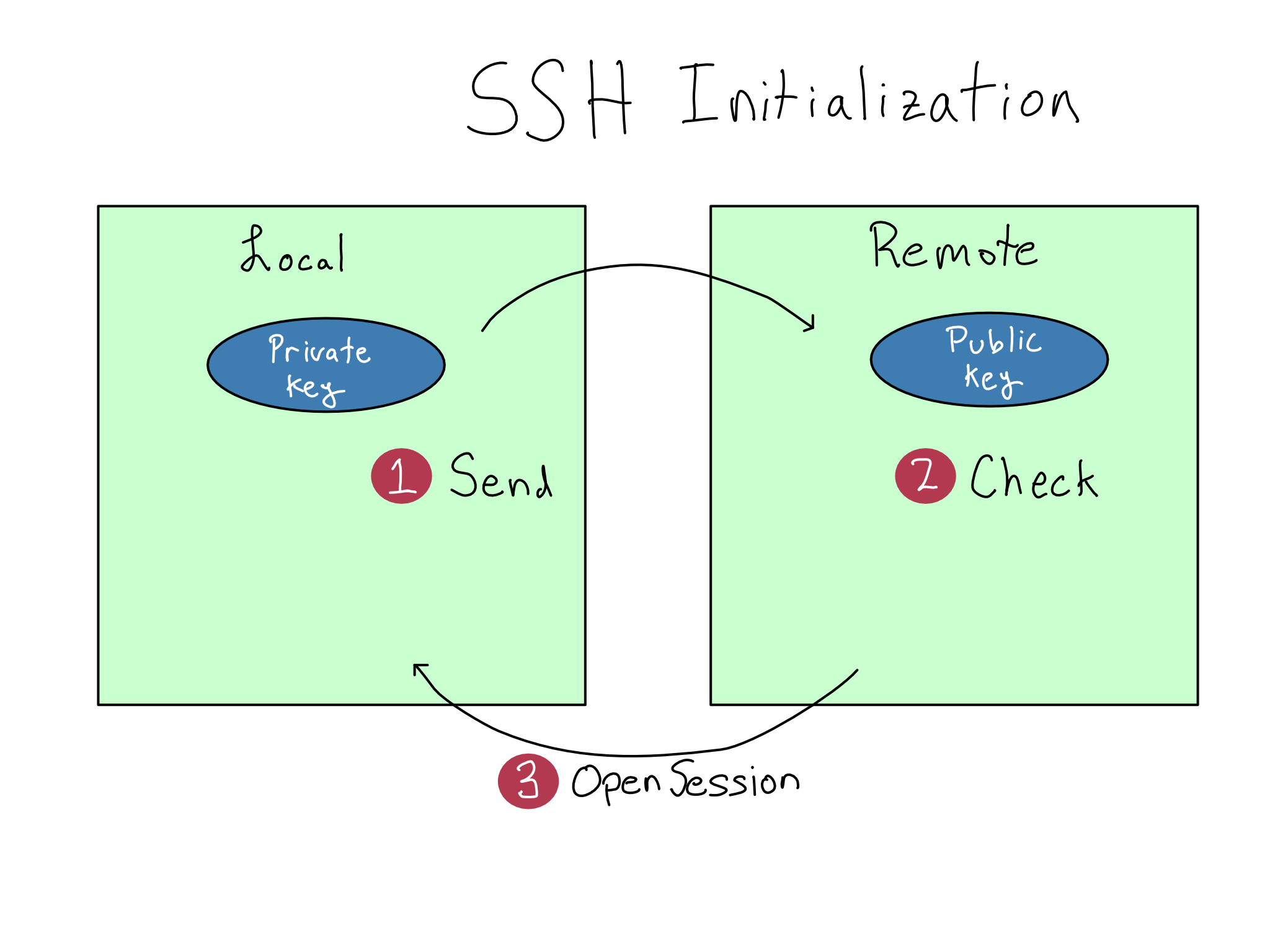
Practical SSH usage
- Step 1: Create a keypair on the machine you are SSHing from. Public key has
.pubsuffix.id_<encryption type>is the standard way to name the key - Step 2: Register a public key to SSH into a server
- Add the public key to the end of your
.ssh/authorized_keysfile in your home directory
- Ensure the permissions on the
authorized_keysfile are correct
- Add the public key to the end of your
- Step 3: To use SSH, type
ssh <user>@<host>- You can specify a particular key with the
-iflag
- Set up an SSH config file if you use SSH a lot. That would shorten
ssh -i my-ssh-key alex@server.example.comtossh alex-server
- You can specify a particular key with the
Continuous connection and debugging
- SSH blocks the terminal it’s using and the connection will break when your computer goes to sleep
- Use
tmuxcommand line utility to:- Put sessions into the background
- Make sessions durable through sleeps and other operations
- Put sessions into the background
- For debugging SSH: Add a
-vto your command for verbose mode- Add another v for more verbosity with
-vv, and if that’s not enough, add another v for super verbose mode
- Add another v for more verbosity with