Function factories
Learning objectives:
By the end of today’s session, you will be able to:
- Identify function factories
- Understand how function factories work
- Learn about non-obvious combination of function features
- Generate a family of functions from data
What is a function factory?
A function factory is a function that makes (returns) functions
Factory made function are manufactured functions
Why function factories work
Function factories are powered by three features of the R language:
R has first-class functions
R functions capture the environment in which they are created
R functions create a new execution environment
Diagramming function factories
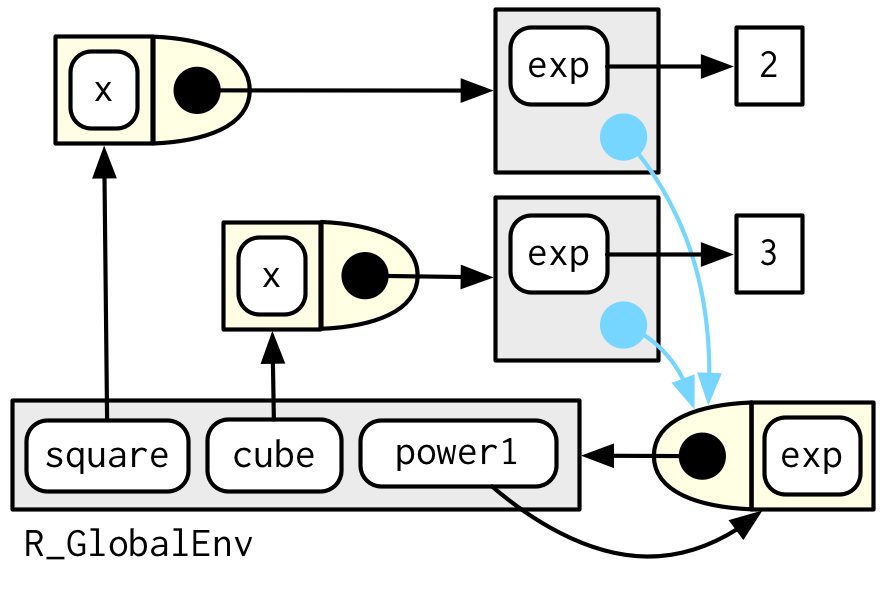
Diagramming function factories
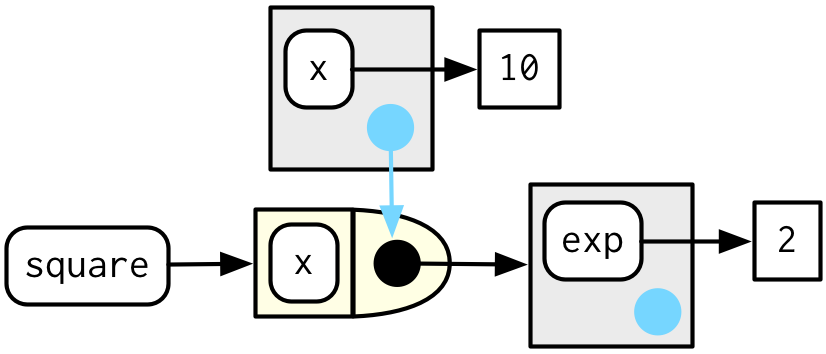
Forcing evaluation
- Beware of changing bindings between creation and execution of manufactured functions
Stateful functions
Garbage collection
- Manufactured functions hold on to variables in the enclosed function factory’s environment
Function factories + functionals
- Combine functionals and function factories to turn data into many functions.